* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SPH 4A - mackenziekim
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Aluminium-conductor steel-reinforced cable wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
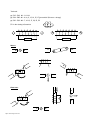
SPH 3U ELECTROMAGNETISM Review 1. From where does all magnetism originate? 2. Draw domains in a highly magnetic bar of steel. Describe how domains can be used to explain what is produced when a bar magnet is broken in half, or when a magnet loses its magnetic strength. 3. Sketch the pattern of the magnetic field (include the poles)around: a) a bar magnet b) an electromagnet 4. What is the more correct term for the north pole of a bar magnet? How was it so named? Why is the “north pole” of the Earth misnamed? 5. Name three elements that make good magnets. These materials are known as what type? 6. Describe the basic principle of electromagnetism. 7. What is the right-hand rule (RHR) for a straight current-carrying conductor? 8. Explain the RHR for a coiled conductor. Sketch a solenoid / helix with the current direction, the m/f lines and the poles. Does current originate from the positive or negative terminal of a battery? How can you change the polarity of the electromagnet (3 ways)? How can you change the strength of the electromagnet (3 ways)? 9. Why would you use a piece of soft iron in a junkyard electromagnet instead of a piece of steel? 10. Sketch how an electric bell operates. 11. What is the motor principle / effect? What is the RHR for the motor principle? 12. What is another name for the electromotive force ? 13. A current-carrying conductor is in the presence of a magnetic field. Sketch the m/f lines that illustrate how an electromotive force is produced. 14. Explain using a diagram how a speaker uses the motor effect to operate. 15. From a diagram, identify the parts of a simple single-loop DC motor including the armature, split ring commutator, brushes, magnetic field and current carrying conductor. How does the motor overcome the gap in the commutator? Why is there a gap there? 16. Show the direction of spin for an armature inside a magnetic field. Include the current flow and the magnetic poles. 17. What is Faraday’s law and electromagnetic induction? What is required for current to be continuously produced? 18. List all the different (but really similar) ways current can be induced in a conductor. 19. How can the voltage induced in a solenoid be increased (2 ways)? 20. Outline Lenz’s Law (describes the direction of the induced current). 21. Compare and contrast DC motors with DC generators. 22. How does a transformer function? Why is AC necessary for its operation. Use a diagram. 23. What are step-up and step-down transformers? How are they useful? 24. If a transformer has 80 primary windings and 400 secondary windings, and 5.0 A is supplied with an electric potential of 110 V, what is the output voltage and current? 25. How did the use of a transformer influence the decision to transmit AC instead of DC? 26. Who are these people and what do they have to do with electromagnetism? a) Michael Faraday b) Nikolai Tesla \sph3U\electromag\582751572 Textbook: pp. 542 – 543: #1 – 8; 11-16 pp. 584 – 585: #1 – 4; 6c, 9, 12, 14, 15, 17 (potential difference = voltage) pp. 590 – 593: #4 – 7; 10-13, 17, 29, 51, 52 Fill in the missing information: S - N + Motors N X S S X N N S S N Generators N S G S \sph3U\electromag\582751572 X N N












![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)





