* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside Earth - Davis` Dazzlers
Survey
Document related concepts
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
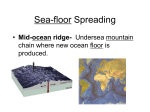
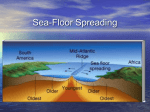
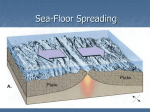
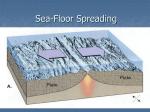
Inside Earth: Chapter 1: Plate Tectonics Section 4: Sea-Floor Spreading Vocabulary: Mid Ocean Ridge: The longest chain of mountains in the world; runs under Earth’s oceans Sonar: device used to map mid-ocean-ridge; bounces sound waves off underwater objects and records the echoes of their sound waves Sea-Floor Spreading: a process that continuously adds new material to the ocean floor Deep-ocean trenches: deep underwater canyons that forms where the oceanic crust bends downward Important Facts: Sea Floor Spreading o At the mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. The molten rock cools and forms new land (salt) as the plates move. The older plate sinks below the other plate and can make mountains and/or islands which will be volcanic o Force within Earth allows new oceanic crust to form (convection current) o Iceland is a part of the mid ocean ridge that is above sea level (island) o Younger ocean floor near the Mid-Ocean Ridge; less dense rock o Older ocean floor near trenches; further away from mid ocean ridge; more dense rock EVIDENCE OF SEA-FLOOR SPREADING Molten Material: Found in the middle of the Mid-Ocean Ridge. The newest molten material pushes the old material away. Scientists have seen this lava erupting and they call it pillow lava. Drilling Samples: The newest molten material pushes the old material further away from the MOR. Therefore, the newest molten rock is found closer to the mid-ocean ridge and the older material is found farther away (moving toward trenches). Magnetic Stripes: The rock of the ocean floor shows the direction of the magnetic force. When the rock cools the iron in the rock leaves a magnetic memory. The ocean floor has magnetic striping that show reversal of the magnetic field.