* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 5: Genetic interactions and epistasis A. Epistasis in a
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
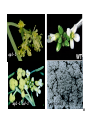
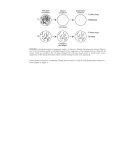
Lecture 5: Genetic interactions and epistasis A. Epistasis in a biochemical pathway B. Epistasis in a regulatory pathway C. Additive interactions D. Synergistic interactions E. Suppressions 1 epistasis analyses (genetic interactions among different mutations) A. Flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in maize CHI C2 CHALCONE FLAVANONE F3H A1 A2 FLAVAN-3,4-DIOL DIHYDROFLAVONOL BZ1 GLUCOSIDE BZ2 bronze ANTHOCYANINS Mt1, Mt2 Peonidin-3-(p-coumaroyl)rutinoside-5-gluciside red2 2 WT: Mutations in c2, a1, a2: Mutations in bz1, bz2: Red Colorless bronze Double mutants C2/a1: colourless-but uninformative bz1/a1: colorless-a1 comes before bz1 bz2/a1: colorless-a1 comes before bz2 For biosynthetic pathways, the phenotype of the earlier gene in the pathway shows in the double mutant. ie. the earlier-step mutant is epistatic to the late-step mutant Determine relationship between a1 and c2 by feeding experiment: add flavanone (naringenin): c2+naringenin = red a1+naringenin = colorless 3 Fig. 7.20 Biochemical Pathways Fig. 7.20 See p214-215 of the textbook 4 4 B. Regulatory pathways Signal A B C D gene expression Positive action-stimulate next step. Null mutation makes insensitive to signal Negative action-represses next step. Null mutation makes the gene turned on at all time (constitutively) b-: gene expression never turned on even in the presence of the signal d-: gene expression constitutively on even in the absence of signal b-d- = d- : constitutively on For regulatory pathways, the phenotype of the later-acting genes shows in the double mutant. 5 ie. the later-acting mutant is epistatic to the earlier-acting mutant 5 wt wt ethylene air ctr1 ein2 air ethylene etr1 ctr ein2 :? Ethylene CTR1 (Kinase) EIN2 triple response For regulatory pathways, the phenotype of the later-acting genes shows in the double mutant. ie. the later-acting mutant is epistatic to the earlier-acting mutant 6 C. Additive pathways Double mutants of dissimilar phenotypes produce a combination of both phenotypes Indicate that the two mutations are in genes acting in separate pathways ap2-2 (flower abnormal) X gl (no trichome) ap2-2 gl double mutant abnormal flower and no trichome 7 ap2-2 gl1 8 D. Synergistic interactions (enhancement) Two genes may act at the same step of a pathway Or in parallel or (redundant) pathways E. Suppression Intrgenic suppressors Extragenic suppressors 9 ap1-1 ap1-1 cal-1 ap1-1 cal-1 10 10 E. Suppression Intrgenic suppressors Extragenic suppressors Allele-specific suppression 11