* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: Target Markets: Segmentation and Evaluation
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Music industry wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
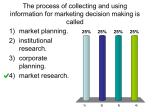
Chapter 4 Marketing Research Marketing Information and Customer Insights Managing Marketing Information 4-10 Marketing Research Steps in the Marketing Research Process Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 4-21 Marketing Research Defining the Problem and Research Objectives Exploratory research Descriptive research Causal research Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 4-22 Marketing Research Developing the Research Plan Secondary data is information that already exists somewhere, having been collected for another purpose. Primary data is information collected for the specific purpose at hand. Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 4-25 Marketing Research Gathering Secondary Data Disadvantages - data may not be Advantages Relevant Lower cost Obtained quickly Accurate Cannot collect otherwise Current Impartial Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 4-26 Marketing Research Primary Data Collection Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 4-28 Marketing Research Implementing the Research Plan • Collecting the information • Processing the information • Analyzing the information Interpreting and Reporting Findings • Interpret findings • Draw conclusions • Report to management Copyright © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. 4-38 Sales Forecasting SALES FORECASTING Who is affected by it? Ops – raw materials, support for existing products, warehousing, production equipment Finance – inventory, all finance statements and expectations, Wall Street Guidance Marketing – mix variables drive forecast and are effected by it, etc. Sales force – budgets, territory sized and # of reps, sales support, customer service HR – hiring in Ops, Mktg, Sales, all parts of the company, R&D – existing product support, new product investments ($ and direction of investment) All budgets across the company flow from sales budget Impact of Erroneous Sales Forecasts Forecast Functional area Too high Too low Production excess output, unsold products inadequate output to meet customer demand Inventory Finance Promotion overstock understocks idle cash cash shortage wasted expenditures insufficient expenditures to cover the market Distribution costly, insufficient to sell excess products inadequate to reach market Pricing reductions to sell excess products price increases to allocate scarce products Sales force too many salespeople, high selling costs too few salespeople, market not covered Customer relations money wasted on unneeded activities, resulting in lower profits unsatisfactory due to out-ofstock products Profits lower unit profits since expenses are high lower total profits because market not covered Qualitative Sales Forecasting Techniques Executive/Owner Judgment Surveys Customer forecasting survey Sales force forecasting survey Expert forecasting survey Delphi technique (panel of experts) Quantitative Sales Forecasting Methods Averaging Simple averages Moving (rolling) averages Exponential smoothing Time-Series Analysis Trend Analysis Cycle analysis Seasonal analysis Quantitative Sales Forecasting Techniques Regression Analysis: Predicting sales based on the relationship between past sales and one or more variables Simple Regression: relationship between 1 independent variable and 1 dependent variable (sales) Multiple Regression: shows strength of relationships between multiple independent variables and dependent variable (sales) Caution 1: no one has yet been able to create a formula that guarantees accurate output Caution 2: correlation does NOT equal causation Other Sales Forecasting Techniques Market Tests Making a product available in the marketplace and measuring purchases and consumer responses Test full mix on limited scale Search for test markets that look like your national target, but on smaller scale Assumptive Reasoning (Chain Ratio) Break a problem down into “knowable” parts, then rebuild it using reasonable assumptions for those parts Market Share-Based Forecast 1. Determine the market size a) Actual best; potential if actual is unknown 2. Determine the market share you will obtain a) Excellent justification of share figure(s) b) “We think…” is insufficient 3. Translate share into units and dollars Market share is after-the-fact calculation; measures success of marketing plan and execution Business Plan Sales Forecasting Exhibit #2: Market Quantification Year Tot Mkt Potential (# Customers)* Mkt Growth Market Projection** Share*** Product Annual Unit Sales Unit Price or Annual $ Revenue Weighted ASP Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 * How did you determine your market potential? Identify key sources and assumptions ** Actual market or market potential. How did you determine the growth projection(s)? Identify key sources and assumptions *** How did you determine your market share? Indicate key sources and assumptions **** How did you determine your unit forecast? Indicate key sources and assumptions