* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simple Current Limit Circuit using Transistors
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
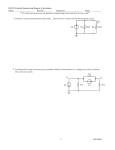
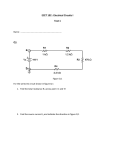
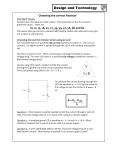
Simple Current Limit Circuit: LOAD +12V 5V R2 Q1 2N3904 The difference between this and the previous circuit is GND 1K This circuit will limit the current through the load to about 50ma. As before when the input to the base resistor is 5V Q1 turns on and current flows through the load. When the input is low Q1 is off and no current flows through the load. Q2 2N3904 R1 14 GND the addition of R1 & Q2. R1 is used as a current sense resistor. It monitors the current flowing through Q1. The voltage drop across R1 increases as the current through Q1 increases. If the voltage at the top of R1 reaches 0.65V Q2 begins to turn on. Q2 diverts some of the current from the base of Q1 and sends it to ground. This reduces Q1's collector current keeping VR1 to about 0.7V. The above circuit will act like a normal switch as long as the load doesn't try and draw too much current. If the load tries to draw too much current (50mA in this case) Q2 will divert some of the current away from Q1 and Q1 will increase the collector emitter voltage drop until the current is stable at about 50mA. Calculations: Let's say that Q2 turns on at 0.7V (it varies a little but this is close enough). We want to limit the current through the load to 50mA. The voltage drop across R1 should be 0.7V@50mA. R1 = V/I = 0.7V/0.05A = 14Ω. Q1's base resistor is calculated the same as before but now you have to add in the extra 0.7V drop across the resistor. Since the worst case gain is 30 the base current should be: Ib = IC/30 = 50mA/30 = 1.7mA. We'll use 3mA so we have a safety margin. R2 = (V – Vbe – VR1)/Ib = (5V – 0.7V – 0.7V)/3mA = 1.2KΩ. We'll use a 1KΩ (close enough). Power dissipation: Make sure you're transistor can dissipate the needed power in the worst case situation. If I short out the load with a wire (0Ω) almost the entire supply voltage (11.3V) will be dropped across the collector emitter junction of Q1 at 50mA. P = VI = 11.3V * 0.05A = 0.565W (quite a bit for the 2N3904). Note: One reason to have a current limit is to protect the power supply incase the output gets shorted to ground. Without a current limit circuit a shorted power supply would most likely blow of fuse or melt a winding on the transformer (killing the supply). Always adjust the current limit on the bench power supply to only provide slightly more current than you think you need. This should keep you from destroying IC's & transistors when wired incorrectly.