* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Station A 1. Why are polar water molecules attracted to other polar
Survey
Document related concepts
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
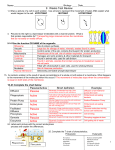
Station A 1. Why are polar water molecules attracted to other polar molecules? 2. Name two biomolecules that have phosphorus in them. 3. What are the three types of R groups that are on amino acids? Station B 1. What is the difference between a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid? 2. What is the difference between an RNA nucleotide and a DNA nucleotide? 3. Two monomers, each with the chemical formula C2H4N5O3, join together in the process of dehydration synthesis. What is the chemical formula of the resulting polymer? Station C 1. Where does an allosteric inhibitor bind onto an enzyme, and how does it affect enzyme function? 2. Which biomolecule is an enzyme composed of? What are its monomers called? 3. Why does an enzyme stop working when placed at a high temperature? 4. If an inhibitor was added to an enzymatic reaction, there would be an accumulation of ____________. Station D 1. How is water attracted to other water molecules? 2. What is the process of evaporation through a plant’s leaf called? 3. Where is N2 found, and where is NO3 found? 4. What is one way N2 is converted into NO3? Station E 1. How does CO2 in the atmosphere endanger marine animals? 2. Why can water not cross the cell membrane without protein channels? What are these channels called? 3. Which process adds phospholipids to the cell membrane, and which process takes phospholipids away from the cell membrane? Station F 1. What does cholesterol (shown below) do to the fluidity of the cell membrane? 2. Which molecule is required when a protein channel wants to transport a molecule across the membrane from low concentration to high concentration? 3. How does an enzyme work to promote a chemical reaction?