* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD STUDIES
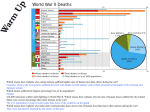
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
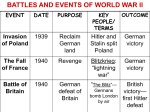
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
WORLD STUDIES World War II: Extra Review 1. New Deal Proposed by Franklin Delano Roosevelt Series of laws to relieve and reform America during the Great Depression Great Depression in America spread to a worldwide economic depression Worldwide depression led to the rise of dictators in Italy and Germany 2. Worldwide Depression Major cause for rise of 1930s dictatorships Made worse by countries raising TARIFFS against each other 3. League of Nations International body of nations formed by Treaty of Versailles Lacked a military unit to enforce its decisions Responded to aggression before WWII by condemning the aggressors but doing nothing about it 4. Fascism Type of government that glorifies the state/nation Relies on dictatorship/authoritarian leadership – ends political disputes People who disagree are locked away and/or killed Highly nationalistic and militaristic Ex. Italy under Mussolini, Germany under Hitler 5. Totalitarianism Government that controls all aspects of people’s lives Ex. Germany under Hitler, Soviet Union under Stalin Government control of media - propaganda Spying and secret police to remove opposition 6. Nuremberg Laws Passed in 1935 Deprived German Jews of citizenship 7. German Violating Treaty of Versailles Rearmed itself – building weapons that were banned (i.e. U-boats) Remilitarized the Rhineland Took over Austria (anschluss was forbidden) 8. Munich Conference Meeting to decide the fate of the Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia Britain and France agreed to allow Hitler to occupy the Sudetenland Appeasement – giving into an aggressor 9. Nazi-Soviet Pact Nonaggression agreement between Germany and Soviet Union Secretly, they agreed to divide Poland Gave Germany freedom to invade Poland 10. Blitzkrieg Lightning war Begins with Luftwaffe (German air force) attacking Followed by fast-moving tanks and troops Targeting weak enemy points – breaking through enemy line Surrounding clusters of enemy army 11. Invasion of Poland September 1939 Began WWII in Europe Germany used blitzkrieg German and Soviet Union split Poland Soviet Union also invaded Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania 12. Miracle of Dunkirk – spring 1940 Germany launched surprise through Ardennes Forest, Belgium Bypassed Maginot Line (French line of super fortresses) Pinned Allied forces on the English Channel at Dunkirk Successful evacuation of Allied troops across the Channel to England – lived to fight another day 13. Vichy Regime France fell to the Germans in spring 1940 Northern part occupied by German Army Southern part was a puppet government called VICHY government Capital was Vichy, France 14. German Invasion of Soviet Union - 1941 Violated the Nazi-Soviet Pact Hitler wanted access to its natural resources Germany invasion halted by harsh Russian winter One of Hitler’s biggest mistakes; major factor in Germany losing war 15. Battle of El Alamein - 1942 Allied victory in North Africa Stopped the German advance in North Africa – led to German and Italian evacuation 16. Tehran Conference 1943 Meeting of FDR, Churchill, and Stalin – The Big Three Stalin dominated the conference and won concessions FDR and Churchill agreed to open up a front against German on the western front (i.e. France) This pushed the Allies to launch D-Day Prior to this, at another meeting, the Big Three agreed to win the war in Europe first before focusing on Asia 17. D-Day Allied invasion of Normandy – June 6, 1944 Fulfilled promise by FDR and Churchill to open up a western front against Germany Major success – many Allied troops landed, opened area to bring in supplies German air force could not support the army as it was low on fuel (Germany running low on supplies 18. Battle of the Bulge German counterattack against Allied advance from the west Named for the bulge it caused in the Allied line in Belgium Held up Allied advance toward Germany Resulted in many casualties for Allies and Germany 19. Embargo Refusal to trade natural resources with Japan (ex. Oil, steel) Japan would have run out of supplies and lost control of its empire Pushed Japan to launch attack on U.S. Pacific Fleet at Pearl Harbor 20. Home Front U.S.A. Efforts taken by American citizens to help the war effort Rationing of goods Reconfiguring factories to make weapons and ammunition Buying war bonds Rosie the Riveter – symbol of American women working in factories 21. Island hopping Allied strategy in the Pacific Picking certain islands for amphibious invasions while bypassing others Resulted in northward progression toward Japan 22. Japan in World War II Fiercely determined Governed by bushido Wanted to build and keep an Asian empire Willingness to fight to the death Kamikaze – suicide pilots who flew bomb-laden planes into U.S. aircraft carriers Defeated by island hopping strategy, heavy bombing, and dropping of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki – Japan surrendered Emperor Hirohito forced to admit that he was human (not a god) 23. Atomic Bombs Truman’s decision – drop bombs or amphibious invasion of Japan Drops two bombs – Hiroshima – August 6, Nagasaki – August 9 Warning given to Japan– “Surrender unconditionally or face immediate destruction” Ended the war in the Pacific – caused Japan to surrender Caused 110,000 Japanese deaths immediately, no American lives lost Saved America and Allies from having to launch D-Day style invasion of Japan – would have caused many more Japanese and American deaths – Japan would fight to the death Gave America more bargaining power at negotiation table with Soviet Union after the war Long-term psychological effects on Japan – devastating destruction of life and property, horrible injuries Long-term radiation effects – sickness, miscarriages and babies born with birth defects, cancer for years to come 24. Holocaust Mass extermination of Jews and other groups by Hitler Plan to fulfill Hitler’s dream of master race Planned and recorded in great detail – concentration camps, work camps, extermination camps Unlike any genocide in history 25. Truman Doctrine Cold War policy of containment Containment – preventing communism from spreading to other nations