* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download POWER POINT for Plenary Session NGs2
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
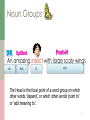
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
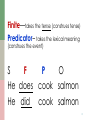
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
1 Wuzzles Temp era ture T I S T I S T I S Falling Temperature 2 English Grammar 1 Lecture 3 Jan 22, 2016 Noun Groups Post-modification Rankshifted clauses Class Activity: Red/Green Challenge 3 Lecture Plan 1. Review key concepts 2. Noun groups a. Post modification b. Down-shifted clauses 3. ACTIVITY/COMPETITION 4 Grammatical Ranking Text Joined clauses Single Clause Word group (joined words) Word Morpheme 5 Review: Noun Groups 6 Which are Noun Groups? A large Italian man drinking a cappuccino Screaming loudly Silly people with nothing better to do Skipping briskly An amazing insect with large scaly wings 7 Find the HEAD of the NG A large Italian man drinking a cappuccino Screaming loudly Silly people with nothing better to do Skipping briskly An amazing insect with large scaly wings 8 Find the HEAD of the NG A large Italian man drinking a cappuccino Screaming loudly Silly people with nothing better to do Skipping briskly An amazing insect with large scaly wings 9 Noun Groups An amazing insect with large scaly wings dv Adj N pp The Head is the focal point of a word group on which other words ‘depend’, or which other words ‘point to’ or ‘add meaning to’. 10 Modifiers: FUNCTION Modifiers tend to add information about the noun. Adjectives, other nouns, or participles, normally perform the function of Modifier before the Head noun, and relative clauses and prepositional phrases often function as Modifier after the Head noun. Pre-Plenary Challenge #1 Can we add “very” in front of hideous? Pre-M Post-M hideous Thomas who loves to eat silly sausages 12 Pre-Plenary Challenge #1 Can we add “very” in front of hideous? YES Pre-M Post-M Ep hideous Thomas who loves to eat silly sausages Adj. noun Relative clause 13 Pre-Plenary Challenge #2 Post-M people who aren’t very smart Relative clause 14 Pre-Plenary Challenge #3 homework helps people who aren’t very smart 15 Pre-Plenary Challenge #3 S F/P O II I homework I helps I people who aren’t very smart I II NG VG NG 16 What’s this F/P stuff??? 17 Finite—takes the tense (construes tense) Predicator– takes the lexical meaning (construes the event) S F P O He does cook salmon He did cook salmon 18 S F P O He does cook salmon S He F/P O cooks salmon S F P O He did cook salmon S F/P O He cooked salmon 19 20 POST-modification in NGs Noun Groups The Monarch is a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. How many NGs in the clause above? The Monarch is a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. 22 Noun Groups Identify the HEAD The Monarch a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. 23 Noun Groups Identify the HEAD The Monarch a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. 24 Noun Groups Identify the Pre-modifiers and label the FUNCTIONS (above) and CLASS (below) a common poisonous butterfly Functions: CLASS: •DR •Pre-M 1 (ep) •Head •dv •Adj •noun 25 Noun Groups Identify the Pre-modifiers and label the FUNCTIONS (above) and CLASS (below) DR Epithet Epithet H a common poisonous butterfly dv adj adj noun Check MOODLE for more information on Epithet and Classifier. DO NOT PANIC. Epithet will do just fine. 26 Noun Groups Identify the POST modifier butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. 27 Noun Groups Identify the POST modifier Label the CLASS (under the wording) H Post-M (qualifier) butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. noun relative clause The relative clause is functioning as the post modifier for the head, butterfly 28 Noun Groups The Monarch is a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. Are there two clauses in this sentence? [How many verbs are there?] dwei Are the two clauses functioning at the same level? Bu dwei 29 Text Joined clauses Single Clause The Monarch is a butterfly… Word group that eats poisonous milkweed Its not at the same rank or level; it is shifted down. Word Morpheme 30 Downshifted/ rankshifted clause The Monarch is a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. …that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage = a relative clause What is its function in the sentence? 31 The Monarch is a common poisonous butterfly that eats poisonous milkweed in its larval stage. The “that” clause ADDS information to the HEAD, butterfly The “that” clause is giving the reader more insights about the butterfly. It is not the main clause. It is downshifted; 32 downranked; rankshifted Functioning within a word group Find examples of a word group (NG) with a rankshifted clause. Find the H; then Pre/Post modifiers the course which is required for graduation the course everyone fears 33 Functioning with a word group Find examples of a word group (NG) with a rankshifted clause. (Find the HEAD) DR H Post-M the course which is required for graduation DR H Post-M the course everyone fears 34 Functioning with a word group Find examples of a word group (NG) with a rankshifted clause. (Find the HEAD) DR H Post-M the course which is required for graduation dv n relative clause DR H Post-M the course everyone fears dv n [which] ellipsed relative clause 35 NGs The first year students are taking the course which everyon e The first year students are taking the course. The first year students are taking the course which everyone fears. (additional information about “course” which happens to contain a VERB and is therefore a clause but functioning at the word group level). 36 Rank-Shifted Clauses A rankshifted clause is one which is not functioning at Clause level. The rankshifted clause is functioning within a word group. Thus, the clause is ‘down-ranked’ from clause to word group level. Other terms: DOWNSHIFTED 37 Text Joined clauses Single Clause The first year students are taking the course.. Word group [which] everyone fears. Word Morpheme 38 This is the silly little dog *who likes to sit on my foot. The relative pronoun, who, is generally used with human subjects. However, those of us who are dog lovers, tend to personify our pets and use “who”. 39 This is the silly little dog who likes to sit on my foot. Post-M Pre-M my silly little dog who likes to sit on my foot. This is a NG. It has a HEAD. It has premodifications and post-modifications. CAN YOU ALSO SEE A CLAUSE? 40 This is the silly little dog who likes to sit on my foot. Post-M Pre-M my silly little dog who likes to sit on my foot. who likes to sit on my foot. What is the function of this clause? Is it the MAIN clause? Or is it serving another purpose? 41 42 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. What is the social purpose of this text? 43 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. EXPERIENTIAL MEANING: What make up the field of the text? danger, Field:words tarantulas, spider, poisonous, bite, fatal, painful, carefully, kill, fragile 44 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. EXPERIENTIAL MEANING: Are the words primarily everyday, non-technical, or noneveryday and technical? Are they concrete or abstract? High or low frequency words? 45 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. EXPERIENTIAL MEANING: Logical meaning “but” is used two times; because 46 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. Interpersonal Meaning: Pronouns? Evaluative language (opinion)? Modality (degree of certainty)? 47 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. Interpersonal Meaning: Pronouns? “they” reference to spider; “you” personal pronoun; Interpersonal somewhat personal Meaning: reader-writer relationship Pronouns? Evaluative language (opinion)? Not too much more painful; Evaluative language (opinion)? carefully, important, very Modality (degree certainty)? Modality (degree ofof certainty/usuality)? Not often; bare assertions 48 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. Find the most complex NG in the text above. 49 Tarantulas are big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere. They are poisonous, but only bite if they sense they are in danger, and the bite is not often fatal. It is not too much more painful than a bee sting. It is important to handle tarantulas very carefully, not because they can kill you, but because they are very fragile. 50 Unpack the NG big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere DR DR Post-M HEAD 51 Unpack the NG DR DR HEAD Post-M big hairy spiders that live mainly in the Southern Hemisphere adj noun Relative clause downshifted adj 52 Unpack the complex NG a tiny little creature that I found in my shoe What is the HEAD? 53 Unpack the complex NG a tiny little creature that I found in my shoe Underline the pre-m Underline the post -m 54 Unpack the complex NG a tiny little creature that I found in my shoe Label the FUNCTIONS (above) Label the CLASS (below) 55 Unpack the complex NG DR Epithet Epithet H Post-M a tiny little creature that I found in my shoe dv adj adj N Rel. clause Label the FUNCTIONS (above) Label the CLASS (below) 56 Downshifted rel. clauses A tiny little creature found in my shoe A tiny little creature hiding in my shoe A tiny little creature living under a rock Are there relative clauses above? Say YES. 57 Downshifted relative clauses A tiny little creature which I found in my shoe A tiny little creature which was hiding in my shoe A tiny little creature which is living under a rock These are called ELLIPSED clauses. 58 Ellipsed relative clause? The boy who is jumping on the bed is driving me crazy. The boy jumping on the bed is driving me crazy. The girl singing along to the radio is off key. I have one dog who loves to sit on my foot. 59 Take a QUICK break: 10min When you come back: RED and GREEN Activity /competition 60 ACTIVITY/Review (competition) 61 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Are the following boundaries correct? Hold up red for no or green for yes. (Clause constituents = I ; between word groups) II IA I clause I contains a verb I II 62 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) II IA I clause I contains a verb I II Correct answer: II IA clause I contains I a verb I II 63 ACTIVITY: Red or green Are the following FUNCTIONS (above the wording) correct? Hold up red for no or green for yes. S F/P O III A clause I contains I a verb III 64 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Are the following CLASSes correct (below)? Hold up red for no or green for yes. S F/P O IIIA clauseI contains Ia verb III NP VP QP 65 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) S F/P O III A clause I contains I a verb III NP VP QP CORRECT: S F/P O III A clause I contains I a verb III NP VP NP 66 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Is the following HEAD identified correctly? Hold up red for no or green for yes. A clause of any length 67 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Are the following FUNCTIONS correct? Hold up red for no or green for yes. DR Post-M A clause of any length 68 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Are the following CLASSes identified (below) correctly? Hold up red for no or green for yes. DR Post-M A clause of any length dv n vp 69 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Dr Post-M A clause of any length dv n vp CORRECT Dr Post-M A clause of any length dv n pp 70 ACTIVITY: Red or green (yes/no) Are the following FUNCTIONS/ CLASSes correctly identified? Hold up red for no or green for yes. DR Pre-M HEAD Post-M the little dog that was barking dv adj n Relative VP clause downshifted 71 Activity: Red or Green? Are the clause constituent boundaries correct? IIIMy dog who is a purebred I is Inot very brightIII 72 Activity: Red or Green? The longest NG in this clause consists of 3 words. My dog who is a purebred is not very bright. 6 73 Activity: Red or Green? There is a downshifted/downranked relative clause in the example below. Yes (green) or no (red)? My dog who is a purebred is not very bright. 74 Activity: Red or Green? There is a downshifted/downranked relative clause in the example below. Is it underlined/ identified correctly. Yes or no? My dog who is a purebred is not very bright. 75 Activity: Red or Green? Are the clause constituent boundaries correct? III This is I a crazy loud plenary held on Fridays. III 76 Activity: Red or Green? Are the clause constituent boundaries correct? III This I is I a crazy loud plenary held every Friday. III 77 Activity: Red or Green? Are the FUNCTIONS correctly identified? S F Cs III This I is I a crazy loud plenary held every Friday. III 78 Activity: Red or Green? Are the CLASSES correctly identified? S F Cs III This I is I a crazy loud plenary held every Friday. III NG VG Object NG 79 Activity: Red or Green? Is the NG correctly identified? DR Ep Ep H Post M a crazy loud plenary held every Friday 80 Activity: Red or Green? Is the NG correctly identified? DR Ep Ep H Post M a crazy loud plenary held every Friday dv adj adj noun vp adv head 81 Activity: Red or Green? Is the NG correctly identified? DR Ep Ep H Post M a crazy loud plenary held every Friday dv adj adj noun vg 82 Activity: Red or Green? Is the NG correctly identified? DR Ep Ep H Post M a crazy loud plenary held every Friday dv adj adj noun [which is] rel clause 83 Activity: Red or Green Is the following statement true (green) or false (red)? Mrs. Keh has three dogs. Mrs. Keh has three boys. Mrs. Keh has three ears. 84 85 What we covered Noun Groups Modifiers Head Nouns Classes of Nouns Functions of Noun Groups Clauses functioning at the word group level (downshifted/rankshifted) 86 HOMEWORK TEXT Whales are large, intelligent, aquatic mammals. They breathe air through blowhole(s) into lungs (unlike fish who breathe using gills). Whales have sleek, streamlined bodies that move easily through the water. Whales swim by moving their muscular tail (flukes) up and down. Fish swim by moving their tails left and right. The biggest whale is the blue whale which grows to be about 94 feet (29 m) long - the height of a 9-story building. These enormous animals eat about 4 tons of tiny krill each day, obtained by filter feeding through baleen. Adult blue whales have no predators with the exception of man. Complex whale songs can be heard for miles under the water. The humpback's song can last for 30 minutes. Baleen whales sing low-frequency songs and toothed whales emit whistles and clicks that they use for echolocation. The songs are thought to be used in attracting mates, to keep track of offspring, and for the toothed whales to locate prey. 87 Reminder: Week 4 Quiz #1 During your Tutorials February 2,3 or 4 You will be given a short text from which the quiz items are taken. II Clause constituents II S, F/P (given) O, C, A NG, VG, Adjg Functions DR Epithet Class. H Class dv, adj (participle), noun, pp, rel. clause 88 Where can you go for extra practice? MOOoodle 89 90