* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A dependent clause
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
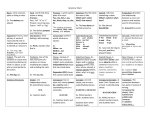
Clauses An independent clause is a group of words that contains a subject and verb and expresses a complete thought. It is a complete sentence. A dependent clause is a group of words that contains a subject and verb but does not express a complete thought. It is depending on an independent clause. A dependent clause by itself is a sentence fragment. Types of dependent clauses Adjective Clauses: An adjective clause modifies a noun or pronoun. It tells what kind, which one, how many, or how much. Adjective clauses are usually introduced by relative pronouns: who, whom, whose, that, which Example: Student volunteers read stories to the children who were in the daycare center. ( The adjective clause modifies the noun, children.) Adverb Clauses: An adverb clause modifies a verb, and adjective, or an adverb. It might tell where, when, how, why, to what extent, or under what conditions. Adverb clauses are introduced by subordinating conjunctions such as if, because, even though, than, so that, while, where, when, as if, and since. Examples: They were happy because they were going to the zoo. (The adverb clause modifies the adjective happy.) The zoo closed earlier than they expected. ( The adverb clause modifies the adverb earlier.) When the field trip ended, the volunteers took the children back to the daycare center. The volunteers took the children back to the daycare center when the field trip ended. *****An adverb clause should be followed by a comma when it comes before an independent clause. When an adverb clause comes after an independent clause, a comma may or may not be needed before it. Noun Clauses are used as a noun. They can serve as a subject, a direct object, an indirect object, an object of a preposition, or a predicate noun. Words that introduce noun clauses: that, how, when, where, whether, why, what, whatever, who, whom, whoever, whomever, which, whichever. ***If you can substitute the word something or someone for a clause in a sentence, it is a noun clause. Examples: Volunteers know that physically challenged people do not want special treatment. (Volunteers know something.) Christopher will tell whoever is volunteering the locations of the elevators. (Christopher will tell someone.)