* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics: A Scientific Revolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
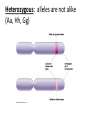
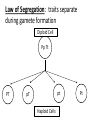
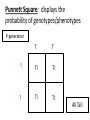
Genetics: A Scientific Revolution Vocabulary: Gene: a segment of DNA which codes for a trait Alleles: one of two versions of a gene Ex. - Tall vs. short - Brown eyes vs. blue eyes -Expressed with letters (WW, Ww, Bb) Heredity: transmission of traits from parents to offspring Inheritance: genes acquired by offspring Genotype: alleles that an organism inherits from its parents bb Bb Bb, BB Phenotype: appearance of an organism as a result of genotype Genotype: bb Phenotype: blue eyes Genetics: field of biology devoted to understanding the patterns/processes of inheritance Gregor Mendel: Father of Genetics -born in Austria -entered a monastery at age 21 -studied peas -studied 15 traits over 28,000 generations -ridiculed for his findings Pure Trait: traits that show up generation after generation P – Generation (parental) – produce offspring with a mix of pure traits F1 – Generation (filial) – offspring of the P-generation F2- Generation – offspring of the F1 generation Mendel’s 1st Experiment (Monohybrid Cross) P-Generation: Tall Flower X short flower F1 Generation: (All Tall) Tall X Tall F2 Generation: 75% Tall; 25% short Principle of Dominance Dominant Allele: the allele whose properties are expresses as phenotype Recessive Allele: allele whose properties are not observed Homozygous: when both alleles are alike (HH, hh, BB, bb, AA) Heterozygous: alleles are not alike (Aa, Hh, Gg) Law of Segregation: traits separate during gamete formation Diploid Cell Pp Tt PT pt pT Haploid Cells Pt Punnett Square: displays the probability of genotypes/phenotypes P-generation T T t Tt Tt t Tt Tt All Tall F1 Generation – Tt X Tt