* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sets of Real Numbers (0-2)
Survey
Document related concepts
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
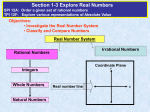
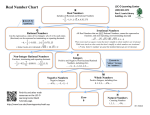
Sets of Real Numbers (0-2) Objective: Classify and use real numbers. Sets of Real Numbers • A number line can be used to show the sets of natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers. • Values greater than 0, or positive numbers, are listed to the right of 0, and values less than 0, or negative numbers, are listed to the left of 0. Sets of Real Numbers Number Set Description Examples Natural Numbers Counting Numbers 1, 2, 3, . . . Whole Numbers Counting Numbers and Zero 0, 1, 2, 3, . . . Integers Whole Numbers and their Opposites . . ., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, . . . Rational Numbers Numbers that can be expressed in the form a/b, where a and b are integers and b 0. 1 23 1 , 0.5, , 0.3 4 41 Irrational Numbers Numbers that cannot be expressed as terminating or repeating decimals, or in the form a/ , where a and b are integers and b b 0. Real Numbers Rational and Irrational Numbers Together 3, 15, 4 10, All Numbers Graph (If Possible) -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 Venn Diagram Real Numbers Rational Numbers Integers Whole Numbers Natural Numbers Irrational Numbers Example 1 • Name the set or sets of numbers to which each real number belongs. 9 10 121 = 11 18 Rational Number Natural Number Irrational Number Real Number Whole Number Real Number Integer Rational Number Real Number Graphing Sets of Numbers • To graph a set of numbers means to draw, or plot, the points named by those numbers on a number line. • The number that corresponds to a point on a number line is called the coordinate of that point. • The rational numbers and the irrational numbers complete the number line. Example 2 • Graph each set of numbers on a number line. Then order the numbers from least to greatest. 1 3 1 7 , , , 1 2 4 4 4 3 25, 4.6, 15, 4 8 7 9 , 2 , 2.1 , 8 10 4 -2 -1 0 1 2 1 1 3 7 1 , , , 2 4 4 4 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.4 4.8 5.2 5.6 6.0 3 15, 4 , 4.6, 25 8 -3.0 -2.8 -2.6 7 9 8, 2 , , 2.1 10 4 -2.4 -2.2 -2.0 Repeating Decimals • Any repeating decimal can be written as a fraction. • Write 0.8 as a fraction in simplest form. – Step 1: Let N represent the repeating decimal. Since only one digit repeats, multiply each side by 10 (If two digits repeat multiply by 100, for three multiply by 1000, etc.). Simplify. N = 0.888. . . 10(N) = 10(0.888. . .) 10N = 8.888. . . – Step 2: Subtract N from 10N to eliminate the part of the number that repeats. Divide each side by the number in front of N. 10N = 8.888. . . Simplify. -(N = 0.888. . .) 8 N 9N = 8 9 9 9 Example 3 • Write 0.23 as a fraction in simplest form. N = 0.232323. . . 100(N) = 100(0.232323. . .) 100N = 23.232323. . . 100N = 23.232323. . . -(N = 0.232323. . .) 99N = 23 99 99 23 N 99