* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of the Generalized Human Cell: Functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
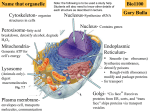
Parts of the Generalized Human Cell: Functions Cell (plasma) membrane ● ● ● ● ● Forms the external barrier of the cell; enables transport of substances into and out of the cell; is involved in intercellular communication; and has receptor sites onto which bacteria, toxins (poisons), or viruses can bind. Microvilli increase the absorptive capacity of the cell. Lysosomes ● ● Digest substances; and destroy harmful or useless tissues and cells. Peroxisomes ● Detoxify poisons. Cytoplasm ● ● ● ● ● Serves as a fluid container for organelles; assists in the movement of organelles and transport within the cell; provides an environment in which chemical reactions can occur; and supports and shapes the cell. Microfilaments form part of the cell’s “skeleton” and are involved in mobility Cilia ● Move together in “waves” to propel substances across the cell’s surface. Flagellum ● Propels the cell. Golgi apparatus ● Rough ER ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Form the bases of cilia and flagella and organize the spindle during cell division. Mitochondria ● Manufacture the cellular energy storage molecules, ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Makes fats, cholesterol, and some hormones; stores energy; detoxifies drugs; and is involved in muscle cell contraction. Ribosomes ● Make proteins. Nucleus ● ● ● ● © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. Makes the building blocks of the cell membrane; and helps to make, store, and deliver proteins. Smooth ER ● Centrioles Prepares and delivers proteins for secretion from cell or use in the cell. Controls and regulates the cell’s activities; transmits genetic (inherited) information during cell division; and provides instructions for protein synthesis. The nucleolus makes ribosomes.