* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reactions of Alcohols
Survey
Document related concepts
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
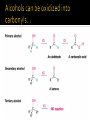
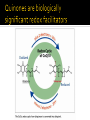
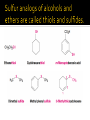
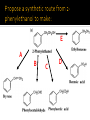
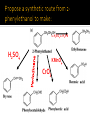
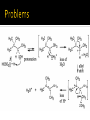
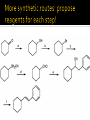
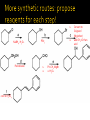
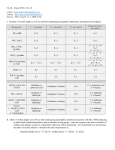
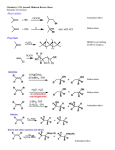
CH21 –AY 2013-2014 SEM II -- R.D. A. Bolinas By protonating –OH in acid, we get an oxonium –OH2+ that can leave as H2O E1/E2 depends on the nature of ROH, but usually E1 prevails, except for 1° alcohols (E2) Predict the major product. Remember Zaitsev’s rule! Predict the major product. Remember Zaitsev’s rule! E1cB occurs in biological systems: the -OH group is two carbons away from a carbonyl (C=O) group We use oxidizing agents: periodinane (with Iodine in +5 oxidation state) PRIMARY R-OH TO ALDEHYDE ONLY We use oxidizing agents: Acidic CrO3/CrO42- (with Chromium in +6 oxidation state) PRIMARY R-OH TO CARBOXYLIC ACID Secondary alcohols will give ketones with either reagent Periodinane Ethers (R-O-R) SN2 reaction between R-X and R-O- SN2 reaction between R-X and R-OWE NEED TO CONSIDER STERIC HINDERANCE. This might lead to E2! Backside attack is not favorable! Methoxide is also a very strong base. Practice: Practice: CANNOT: be dehydrated with acid, convert into halides with HX CAN: convert to ether via Williamson ether synthesis, react via EArS (review) The aromatic ring allows the H+ to leave easily, making phenols ACIDIC. Because they don’t have a hydrogen on the COH carbon, phenols become quinones Quinones easily change form into hydroquinones Ethers are unreactive to most common reagents Only strong acids can usually react with them: HI/HBr via SN1 or SN2 Ethers are unreactive to most common reagents Only strong acids can usually react with them: HI/HBr via SN1 or SN2 SN1 Epoxides come from alkenes + peroxy acids High angular strain induces reactivity. SN2 attacks with H3O+ or HX lead to trans-diol or trans-halohydrins, other nucleophiles work too. SN2 attacks with H3O+ or HX lead to trans-diol or trans-halohydrins, other nucleophiles work too. beta-blocker that is used for treatment of cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, and heart attacks SN2 Synthesis: Williamson thioether synthesis http://b.vimeocdn.com/ts/147/230/147230470_640.jpg http://delight.spslinfotechpvtl.netdnacdn.com/media/catalog/product/cache/1/image/650x650/9df78eab3 3525d08d6e5fb8d27136e95/r/e/rebonding.jpg For rebonding: (1) Thioglycolate (acid-like) to convert disulfide bonds in hair protein to thiolates (2) Hydrogen peroxide to oxidize the thiolates back to disulfides. (3) Reforming the disulfides helps re-align amino acids and make hair straight http://delight.spslinfotechpvtl.netdnacdn.com/media/catalog/product/cache/1/image/650x650/9df78eab3 3525d08d6e5fb8d27136e95/r/e/rebonding.jpg “antioxidant” because it protects your cells from oxidative degradation. http://b.vimeocdn.com/ts/147/230/147230470_640.jpg E A B C D 1. H2SO4 2. H2/Pd H2SO4 KMnO4 CrO3 1. conc’d H2SO4 NaBH4, H3O+ PBr3 Periodinane 1. 2. 2. Ph-CH2-MgBr 2. H3O+ Convert to Grignard (Mg/ether) add CH2=O then acid