* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View - Psychology
Survey
Document related concepts
Carolyn Sherif wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
System justification wikipedia , lookup
James M. Honeycutt wikipedia , lookup
Leon Festinger wikipedia , lookup
Vested interest (communication theory) wikipedia , lookup
Implicit attitude wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive dissonance wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
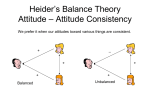
Social Psychology The Theory of Cognitive Dissonance Not only do our attitudes influence what we do, what we do can sometimes influence our attitudes. “Dissonant” means “not harmonious”, conflicting. Cognitive Dissonance is an unpleasant state that can occur when we hold two conflicting attitudes, or when our attitudes conflict with our behavior. The theory says that when we experience dissonance, we immediately (and unknowingly) take steps to reduce it. This often involves attitude change. Changing Attitudes Through Cognitive Dissonance Here’s what can happen if you say something you don’t really believe. · · · · You hold an attitude, X. You say the opposite, not-X, with a minimum amount of justification. Attitude, X, and statement, not-X, are dissonant. To reduce the dissonance, you change your attitude to not-X. You now believe what you said. Classic Experiment on Cognitive Dissonance (Festinger & Carlsmith) Control Group: Performs dull task; Goes for interview; Expresses negative attitude toward the task. Experimental Group: Performs same dull task; Asked to lie to waiting participant and say the task was interesting and fun; Half are paid $1 to lie and half are paid $20; Goes for interview. In the interview, one of these groups ($1 or $20) expressed a negative attitude toward the task (similar to the Control Group’s) while the other group expressed a positive attitude. ? Question: According to the Theory of Cognitive Dissonance, which group should form a positive attitude, and why? Answer: The $1 group should form positive attitude. They said something they didn’t believe with a minimum amount of justification. This prediction was supported.