* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Genetics Notes
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
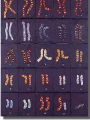
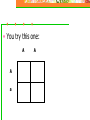
Introduction to Genetics “the study of heredity” • Gregor Mendel • The Father of Genetics • carried out important studies of heredity, used pea plants • Heredity—the passing on of traits from parents to offspring • Trait- a specific characteristic that is controlled by genes • Exp. Eye color, hair color, height All of our “traits” are coded into the DNA that makes up our chromosomes. • Chromosomes • Tightly coiled DNA where your genes are carried • Genes • Sections of DNA that control your traits Homologous Chromosomes Chromosomes that are the same size and shape and carry the same genes. You P get one from your mother and one from Short pea plant Tall pea plant your father that match up. 1 F1 F2 3 tall: 1 short Karyotype • A picture of all the chromosomes contained within a single cell. • Contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of allosomes (sex chromosomes) • Alleles • The different forms a gene can take. (Letters) • 2 Types of Alleles: • 1. Dominant - Represented by a capital letter (Exp. A) • 2. Recessive - Represented by a lower-case letter (Exp. a) • Genotype • The combination of two alleles (letters) that represent the genetic make-up of an individual. (AA, Aa, aa) • Phenotype • The observable physical characteristic of an individual that are the result of its genotype. (Long eyelashes, Blue or Brown eyes) 3 Types of Genotypes: • 1. Homozygous Dominant (purebred) • 2 identical alleles that are capitalized (AA, TT) • 2. Heterozygous (hybrid) • 2 different alleles (Aa, Tt) • 3. Homozygous Recessive • 2 identical alleles that are lower-case (aa, tt) Principle of Dominance • If a dominant allele is present that phenotype is visible • An organism that is recessive for a particular trait will exhibit that form only when the dominant allele is not present. • Organisms with a heterozygous genotype (Aa) will never exhibit the recessive trait because it is hidden (masked) by the dominant allele. Mendel’s Principles • Law of Segregation -• the two alleles for a characteristic are packaged into separate gametes • Law of Independent Assortment -• each pair of alleles segregates into gametes independently The Tall (T) allele in snapdragons is dominant to the short (t) allele. If two heterozygous tall (Tt) snapdragons are crossed, what will be the ratio of short to tall plants? • You try this one: A A a A Question 1 The passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring is __________. A. genetics B. heredity C. pollination D. allelic frequency The answer is B. Genetics is the branch of biology that studies heredity. Question 2 What are traits? Answer A specific characteristic that is controlled by genes. Height, hair color and eye color are examples of traits in humans. Question 3 Gametes are __________. A. male sex cells B. female sex cells C. both male and female sex cells D. fertilized cells that develop into adult organisms The answer is C. Organisms that reproduce sexually produce male and female sex cells, called gametes. Question 4 Which of the following genotypes represents a animal that is homozygous dominant for a trait? a. KK b. Kk c. kk Question 5 Which of the following genotypes represents a plant that is homozygous recessive for height? A. TT B. Tt C. tt