* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Allied War in Europe
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of the United Kingdom during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
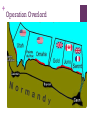
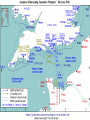
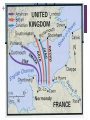
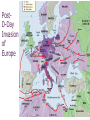
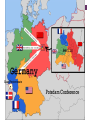
+ The Allied War in Europe + Where we left off… Allies had just gained access to Europe and chased the AXIS powers North where they surrendered in Northern Italy Mussolini is dead Hitler has violated the Non-Aggression Pact and his forces have invaded Stalingrad There is now a war in the East and the West + Invasion of Western Europe To be successful Allies took to the air Just like Germans they targeted cities Carpet bombing- planes scatterd large number of bombs over wide area Bombings of Hamburg - Operation Gomorrah Destroyed many German cities Goal: destroy Germany’s ability to fight a war People took cover in undergrounds City set ablaze More than 40,000 killed American planes bombed by day, British by night + Invasion of Western Europe George Marshall -top American general and FDR’s chief of staff pushed for the attack of German occupied France at every opportunity Operation Overlord - invasion of occupied France General Eisenhower Launched from Great Britain Forces were gathered Polish, Dutch, Belgian, and French joined the British, American and Canadian forces already in place Artillery was in place Machine gun nests, barbed wire, land and water mines and underwater obstructions + D-Day Invasion Some preferred Pas-de-Calais over Normandy; but there were problems. Germans knew an invasion was coming - they just didn’t know when Operation Bodyguard fake Allied plan, to deceive the Germans of timing and location of the allied attack General Patton, Pas-De-Calais and Norway Why do you think having Patton lead Operation Bodyguard was important for the success of the operation? Believable - he was a famous military leader Blow up tanks, trucks, tents everywhere, soldiers “looking busy” (even had people make fake tank tracks) Sent fake messages to be intercepted + D-Day Invasion Under the umbrella of Bodyguard fell Operation Fortitude Convince Hitler Fortitude-North - attack from Norway and Sweden Fortitude-South- attack at Pas de Calais (France) Normandy was thought to be a diversion Even AFTER the Normandy landing Hitler still refused to redirect troops He even took troops from Normandy and moved them to Calais + Operation Success + D-day Invasion Weather, location, forces, secret plans, intel, leaders, etc. All factors contributed to Allies settling on June 6th Especially weather…WHY? + D-Day Invasion - The day of Shortly after midnight on June 6th, 1944 Troops land at the beach at 6:30 am 4,600 invasion crafts and warships slipped out of the English harbor 1,000 British bombers pounded German forces at Normandy 23,000 airborne Brits and Americans parachuted behind enemy lines 5 landing zones selected Juno Beach – Canadian Army Gold and Sword Beaches – Assigned by the British Army Omaha and Utah Beaches – Used by the American forces, Omaha would feature the bloodiest combat. + Operation Overlord + + D-Day Invasion Omaha was the least successful with 2,000+ deaths “it seemed like the whole world exploded. There was gunfire from battleships, destroyers and cruisers. The bomber were still hitting the beaches… As we went in, we could see small crafts from the 116th Infantry that had gone in ahead, sunk. There were bodies bobbing in the water, even out three or four miles” -Lietenant Robert Edlin + Robert Capa Photograpghy The only photographer to go ashore in the first wave of troops to capture the scenes on the beach + D-Day Progress By noon the first few waves of troops had made it onto the beaches and began to secure the coastline By midnight, many Germans had been pushed back and had begun retreating back into the countryside. The beach was important for incoming supplies and support troops This invasion brought 2 million Allies to France PostD-Day Invasion of Europe + Liberating France Allied forces would look to Caen (Con) and Cherbourg next as we attempted to move inland. Battle of Caen Battle Hedgerows Axis take one allied life for each meter they move Operation Market Gardens Secure roads to France Tried to end the war before Christmas of 44 by securing roads unsuccessful- Germans are pretty tough! By mid-September of 44, Allied forces had crossed over into Germany + The Battle of the Bulge Forces began to prepare for winter One of the worst in Belgium history As Allies move in on the Axis, the Germans launched a counter attack that pushed back the Allied line forming a bulge The battle Last just over a month Belgium (Ardennes Forest) Largest battle in Western Europe during WWII and largest battle ever fought by the US army 600,000 GI’s Nearly 80,000 Allies dead Nearly 100,000 Axis dead + The war ends in Europe Nazi leaders recognize the war is over March 1945 - Allies push in towards Berlin from the West and Soviet allies move in from the East Soviets stood to lose the most in WWII with an estimated 18 million (soldier and civilians) April 1945 - Soviets push their way into Berlin Battle of Berlin Last offensive in the European theater This is Stalin’s payback to Hitler + Tragedy strikes Before the Americans can secure V-E day April 12th 1945 - FDR will die Harry S. Truman -33rd President He must negotiate the end of the war Possible problems for the 2nd half of the century + Germany Surrenders April 30th, 1945 - with the city of Berlin surrounded Hitler commits suicide in an underground bunker May 8th, 1945 - Germany surrenders V-E day (Victory in Europe) Still must defeat Japan + + Yalta Conference February of 45 Stalin, Churchill and FDR meet in Yalta (SU city) Formulate a plan for the end of the war and post war Split Germany and Berlin between Allies (SU, US, UK, France) Stalin promised elections in freed territory of Eastern Europe Potsdam Conference Does not Promised to declare war on Japan Holds out as long as he can Saar Protectorate Potsdam Conference