* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Republic
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
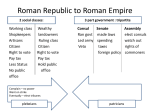
The Roman Republic Chapter 6 Unit 1 Notes The Roman Republic Main Idea: Power and Authority - The early Romans established a republic, which grew very powerful. Why Now: Fundamental values and institutions of western civilization began in Rome The Roman Republic Terms: Republic, patrician, plebeian, tribune, consul, senate, dictator, legion, Punic Wars, and Hannibal Setting the Stage: Rome grew from a small city to a major empire that stretched 3500 miles east and west . It will become the most famous and influential. Origins of Rome 753 BC by Romulus and Remus Sons of the God Mars and a Latin princess They were abandoned on the Tiber River and raised by a wolf They decided to build a city on that spot for its strategic location and fertile soil QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Origins of Rome Rome’s Geography - Built on 7 rolling hills - Mid - location: - It is half way down the peninsula - And half way point of the Mediterranean Sea Origins of Rome The First Romans - 3 groups migrated to Italy - Latins - Settlement on the Palatine Hill (1st Romans) - Greeks - Colonies along southern Italy (center of commerce) - Etruscans - Settle in northern Italy (Rome adopted their alphabet) The Early Republic 600 BC an Etruscan became King of Rome, this is the beginning of Rome’s growth Forum: heart of Roman political life Last King of Rome, Tarquin the Proud (extremely harsh ruler) He was driven from power in 509 BC Rome declared they would never be ruled by a King again Established a REPUBLIC: (from Latin res public, public affairs) form of government in which power rests with the citizens (free born males) who can vote for leaders The Early Republic Patricians and Plebeians - Patricians were wealthy landowners (held most the power) - Inherited power and claimed ancestors gave them the right to rule - Plebeians were commoners (farmers, artisans, merchants) who made up the majority of the population - Eventually were able to vote but not hold public office - In time formed own assembly with elected officials called TRIBUNES: protected the rights of the plebeians The Early Republic The Twelve Tables - Plebeians wanted written laws so the patricians couldn’t interrupt laws to suit them - The Twelve Tables: were carved and hung in the Forum, became the foundations of Roman law - All free male citizens had the right to be protected under the law The Early Republic Government Under the Republic Command army Directed government 300 members from upper class Foreign and domestic policy Eventually plebeians will be allowed in Senate aristocrats advise consuls Consuls two rulers serve 1 year Couldn’t be re-elected for 10 years Centuriate Assembly soldiers only chose consuls Tribal Assembly ordinary citizens makes laws SERVES FOR LIFE One couldn’t over rule the other Comparing Republics ROME USA 2 Consuls elected by Assembly for 1 year, chief of government and head of Army Executive -Senate 300 (life) head of foreign policy and financial policies, and advises Consuls - Centuriate Assembly soldiers (life) selects consuls and makes laws - Tribal Assembly citizens grouped by where they live (life) elects tribunes and make laws Legislative Praetors, judges, 8 chosen for 1 year by Centuriate Assembly Judicial President, elected by the people for 4 years, chief of government and Army -Senate 100 (6 years) make laws and advise president on foreign policy - House of Representatives 435 (2 years) make laws, originates revenues bills Supreme Court, 9 justices, appointed for life by president, highest court Twelve Tables were a list of rules that were the basis of Roman legal code Legal Code US Constitution is the basic law of the USA All adult landowner males Citizenship All native born or naturalized adults Rome Spreads Its Power Rome Conquers Italy - 4th c. Rome dominated Italy (defeated Etruscans and Greeks) - Rome treated all conquered differently: - Latins: Full citizens - Farther from Rome: all rights but no vote - Allies of Rome: just had to supply Roman Army and they would be left alone HELPS BUILD A STRONG AND SUCCESSFUL EMPIRE!!! Rome Spreads Its Power Rome’s Commercial Networks - LOCATION: merchants moved by land and sea - Traded wine and olive oil - Large and powerful Carthage in Northern Africa, once a Phoenician colony, was rising in power and influence - STOOD IN ROMES WAY FOR DOMINANCE OF MEDITERRANEAN SEA Rome Spreads Its Power War with Carthage - Punic Wars: 264-146 BC Rome v. Carthage - 1. Control of Sicily and W. Med. - 26 years - Carthage defeated - 2. Hannibal: Carthaginian general assembled an Army of 50,000 infantry, 9,000 cavalry, and 60 elephants - Wanted to surprise Rome - Almost won, then Rome regrouped - Roman general Scipio decides to force Hannibal home by Rome going to attack Carthage - Carthage is defeated - 3. Rome goes to Carthage and sets city on fire, sells 50,000 inhabitants into slavery - RESULTS: (1) Rome’s dominance in W. Med, (2) empire now stretched from Spain to Anatolia=MORE CHALLENGES QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture.