* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Republic - EDSS Ancient Civilizations
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman tribe wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman consul wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
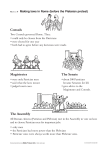
THE ROMAN REPUBLIC ROMAN REPUBLIC (509 BCE) • Resulted from discontent of tyrannical Etruscan monarchy • In a republic, citizens elect leaders to run the gov’t • SPQR = Senatus Populusque Romanus • The Senate and the People of Rome • A combination of aristocracy, oligarchy and democracy NEW ORGANIZATION • Consuls = leaders chosen to replace Kings • Assembly = ordinary citizens who elected the Consuls • Senate = rich men who advised the Consuls • Although citizens elected their own representatives, the Republic was NOT a democracy… every citizen did not have equal power • Divided into 2 classes: patricians and plebeians ROMAN SOCIETY Patricians Plebeians PATRICIANS VS PLEBIANS The internal history of the Roman Republic consisted of constant tension and feuds between these two classes Patricians • Senatorial aristocracy • Landowners • From Latin word “patres” (father) Plebeians • Landless poor • From Latin word “plebs” (common people) PATRICIANS • Wealthiest 10% of Rome’s population • Only ones who could run for political office (magistrates) • Served as priests, lawyers, judges • Granted financial and legal protection to clients • Plebeians, newcomers to Rome, ex-slaves, run-aways (from family) • Held the Roman imperium (power of law and military command) PLEBEIANS • The other 90% who did the “heavy lifting” in society • Till land, herd livestock, craftsmen, tradesmen, labourers • No right of appeal against decision of patrician gov’t since no laws were codified or published • Relied upon patricians exclusively for expertise/leadership • Defended Rome as soldiers PLEBEIAN “TRUMP CARD” • Could engage in “secession” to get what they wanted • Strike and refuse to defend Rome • Plebeians went on strike 5 different times GOVERNMENT IN THE ROMAN REPUBLIC • • • • The Roman Senate Council of most powerful men in Rome Controlled the state budget and foreign affairs Owned most of the land Chosen for life MAGISTRATES • • • • • Consul Most powerful magistrates were the two Consuls (or Chief Magistrates of State) Both had the power to veto (Latin for “I forbid”) each other in important decisions Elected by patricians for a 1-year term Extensive legislative, judicial power Usually commanded the army Cicero Scipio Africanus the Elder Lucius Junius Brutus PLEBEIAN TRIBAL COUNCIL & TRIBUNES • Membership restricted to non-senatorial males • Two plebeian tribunes elected and could veto decisions made by the consuls • Eventually increased to 10 tribunes • Tribunes became powerful interpreters of the peoples’ wishes ROMAN REPUBLIC GOVERNMENT (P.170) • Sketch textbook diagram DAILY LIFE IN THE REPUBLIC (P.180-185) Beliefs Family Life & Morality Education Role of Women Latin Language & Literature