* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Helicobacter pylori evolution and phenotypic diversification in a
Survey
Document related concepts
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
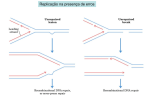
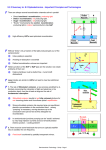
Helicobacter pylori evolution and phenotypic diversification in a changing host Sebastian Suerbaum & Christine Josenhans Asolina Braun 11.01.2010 History - Barry Marshall & Robin Warren, 1982 colonizes the stomach link to gastritis and ulcers Marshall ingests H. pylori => gastritis 2005 Nobel prize - „for their discovery of the bacterium H. pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer disease” Clinics • colonizes 50% of the world‘s population • infection during infancy via family members 5,5% of all cancer cases Success Strategy • extreme genetic diversity – mutagenesis – recombination • host interaction – outstanding evation of immune system – immune suppression Diversity • extraordinary genetic heterogeneity • every infected individual harbors their own strain(s) • strains change during infection • high recombination events (multilocus enzyme electrophoresis data, homoplasy test) Geographical Distribution • data based on multilocus sequence typing Diversification by Mutagenesis • defect mismatch repair • defect base excision repair • long repetitive sequences => – frameshift – altered expression if located inside regulators – intragenomic deletions/rearrangements Diversification by Recombination • recombination of short DNA fragments (~417 bp vs. 2-10 kbp) • 50% exchange of genome in 40 years • 1,111 conserved genes + ~400 • frequent gene exchange • seldom gene loss/gain (1 in 650 events) Host Interaction • BabA and SabA – adhesins – bind Lewis b and sialyl-Lewis on epithelium – phase-variable expression – adaptation to niches, acid conditions, … – geographical correlation with blood groups Host Interaction • vacuolating cytotoxin (Vac A) – vacuolation, tissue damage – inhibits proliferation of T cells – inhibits antigen presentation by B cells • LPS – Lewis antigens (on O-antigen side chains) – binding of H. pylori to DCs via DC-SIGN => TH1 response diminished, ↓IL6, ↑IL10 => immune suppression – heterogenous expression Host Interaction • flagellar motility – implications unknown • cag PAI (a chromosome segment) – type IV SS – destruction of the basal membrane – atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcers, adenocarcinoma (Ishikawa et al., PNAS, 2005) Outlook • prevalence in Western countries declines – due to less mixed infections? – due to better hygiene, antibiotics, broccoli? • vaccination (Cag A) Summary • high prevalence of 50% • extreme genetic diversity – defective mutation repair systems – many repetitive regions prone to mutations – many recombination events • outstanding evation of immune system – – – – BabA and SabA Vac A LPS Cag PAI