* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Differential Mode Op-Amp
Survey
Document related concepts
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
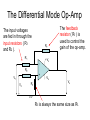
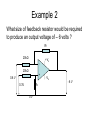
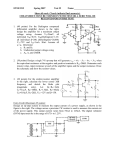
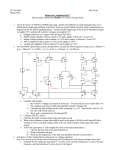
The Differential Mode Op-Amp What is the Differential Mode ? • The op-amp can be connected up in various ways or modes. • What it does depends on how it is connected up. • When connected up in the differential mode, it finds the difference between the two input voltages and multiplies it by the gain. The Differential Mode Op-Amp The input voltages are fed in through the input resistors ( R1 and R2 ). Rf R1 - The feedback resistor ( Rf ) is used to control the gain of the op-amp. +Vs R2 + V1 V2 R3 -Vs Vo 0V R3 is always the same size as Rf. Revision – The Gain of an Amplifier You may remember from Standard Grade that the gain of an amplifier is the ratio of the output and input voltages. 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑔𝑎𝑖𝑛 = 𝑉𝑖𝑛 The gain can also be expressed in terms of the resistors used to connect up the op-amp. 𝑅𝑓 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑔𝑎𝑖𝑛 = 𝑅1 The Differential Mode Gain Equation 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 = 𝑅𝑓 𝑅1 (𝑉2 −𝑉1 ) Example 1 Calculate the output voltage from the op-amp below. 150kΩ 20kΩ - +Vs 20kΩ + 0.3 V 150kΩ 0.5V 0V -Vs Vo Example 1 - Solution 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 𝑅𝑓 = (𝑉2 −𝑉1 ) 𝑅1 150𝑘 = x 0.5 − 0.3 20𝑘 = 1.5V Example 2 What size of feedback resistor would be required to produce an output voltage of – 6 volts ? Rf 20kΩ - +Vs 20kΩ + 0.6 V R3 0.3V 0V -Vs -6V Example 2 - Solution 𝑅𝑓 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 = (𝑉2 −𝑉1 ) 𝑅1 𝑅𝑓 𝑉𝑜𝑢𝑡 ⟹ = 𝑉2 − 𝑉1 𝑅1 −6 ⟹ 𝑅𝑓 = x20k 0.3 − 0.6 ⟹ 𝑅𝑓 = 400kΩ