* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lymphatic system - andoverhighanatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
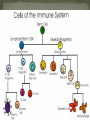
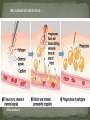
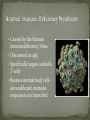
CHAPTER 12 CONSISTS OF 2 PARTS 1. LYMPHATIC VESSELS- transport fluids that have escaped the cardiovascular system called LYMPH 2.LYMPHATIC ORGANS- (lymph nodes)- filter the fluid and kill off invaders with lymphocytes Very similar to veins with lymph capillaries becoming successively larger and eventually called LYMPHATIC COLLECTING DUCTS. Have valves very similar to veins that help to move lymph RIGHT LYMPHATIC DUCT – collects lymph from the right arm and right thorax and right head- drains into the subclavian vein THORACIC DUCT- collects lymph from the rest of body – drains into the sub clavian vein -KIDNEY SHAPED -ABOUT 1 INCH LONG -about 1000 found in the body -contains large amounts of lymphocytes –B cells and T cells -FOUND IN CLUSTERS IN 3 MAJOR REGIONS 1. AXILLARY– (armpit) 2. CERVICAL- (side of neck) 3. INGUINAL- (groin) SPLEEN THYMUS TONSILS PEYER’S PATCHES Located on the left side and curls around the stomach Filters the blood of bacteria, viruses and other debris Breaks down worn out RED BLOOD CELLS so hemoglobin can be reused. Storage site of blood. Produce Lymphocytes Produces hormones- thymosin that programs lymphocytes Located low in the throat More active in youth Lymphatic tissue located in the pharynxTrap bacteria entering the pharynx May become sore and swollen called --- TONSILITIS “tonsils” of the small intestine Capture bacteria that are found in the digestive system. MUCOSA-ASSOCIATED LYMPHATIC TISSUE(MALT) consists of tonsils and Peyer’s patches which protect the respiratory and digestive tracts from never-ending invasion SKINSWEAT contains a low pH level preventing bacterial growth SEBUM- contains chemicals toxic to bacteria VAGINAL SECRETIONS- highly acidic STOMACH- hydrochloric acid is highly acidic SALIVA- contains lysozomes- enzyme that kills bacteria MUCUS- traps organisms from entering the digestive and respiratory systems - New particles take longer to identify, and a person remains ill until a new antibody can be crafted - Old particles are quickly recognized, and a person may never become ill from that invader again. This person is now immune. STEM CELL– undifferentiated cells made in the red bone marrow (can become Lymphocytes or Granulocytes) LYMPHOCYTES NATURAL KILLER CELLS- protect us from tumored cells and virus infected cells B CELLS- (bone cells) lymphocytes that mature in the bone marrow-produce antibodies, help present antigens., and form Memory B cells T CELLS- (Thymus cells) lymphocytes that mature in the thymus- do not produce antibodies– but do release chemicals to spend up phagocytosis by MACROPHAGES- become T HELPER cells that help in the maturity of B cells and Cytotoxic T cells that aid tumored cells and in organ rejection GRANULOCYTES NEUTROPHILS- 1st responder to infection site- “phagocytize” EOSINOPHILS- phagocytize parasites and help with allergic reactions and asthma BASOPHILS– contains vasodilator HISTAMINE and anticoagulant HEPARIN with aide in the INFLAMMATION RESPONSE MONOCYTES- stored in the spleen can become MACROPHAGES or DENDRITIC CELLS 1. INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE- general 2. ANTIGEN SPECIFIC RESPONSE- INFLAMMATION RESPONSE--- (Histamines) Any substance capable of setting off an immune response. Almost all things are ANTIGENIC (including our own cells) but our body had learn to identify our cells and these SELF-ANTIGENS (Human leukocyte antigenHLA) do not trigger an immune response in us. 1. MACROPHAGES-gobble up invading particles and break them up 2. They show the ANTIGEN pieces to T-cells, who identify the pieces 3. T CELLS help to find specific B-cells to help 4. B-cells produce antibodies that are equipped to find that specific antigen on a new cell. 5. Memory B cells are also made- for future attacks also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects like bacteria and viruses May be free flowing or attached to B cells - You produce the antibodies - Your body has been exposed to the antigen in the past either through: - Exposure to the actual disease causing antigen – You fought it, you won, you remember it - Planned exposure to a form of the antigen that has been killed or weakened – You detected it, eliminated it, and remember it What is this second type of exposure called? Antigens are deliberately introduced into the immune system to produce immunity Because the bacteria has been killed or weakened, minimal symptoms occur Have eradicated or severely limited several diseases from the face of the Earth, such as polio and smallpox - Immune system mistakenly recognizes harmless foreign particles as serious threats - Launches immune response, which causes sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes - Anti-histamines block effect of histamines and bring relief to allergy sufferers Caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Discovered in 1983 Specifically targets and kills T-cells Because normal body cells are unaffected, immune response is not launched MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS- immune system attacks the myelin sheath of the nervous system MYASTHENIA GRAVIS GRAVES DISEASE