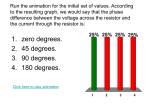
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test1_Spring12 - UTK-EECS
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
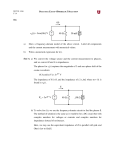
1. The voltage of an electromagnetic wave traveling on a transmission line is v( z, t ) 2ez sin( 4 108 t 2z ) V, where z is the distance in m from the generator and t is time in s. (a) Find the frequency, wavelength, and phase velocity of the wave. (Note: you must get the units right to get full points.) (b) At z = 2 m, the amplitude of the wave was measured to be 1 V. Find . (Note: Again, you must get the unit right.) 2. With an unknown load connected to a slotted air line, a voltage standing wave ratio S = 2 is recorded by a standing wave indicator and minima are found at 11 cm, 19 cm, ...on the scale. When the load is replaced by a short circuit, the minima are at 16 cm, 24 cm, … If Zo = 50 , calculate the wavelength , the frequency f, and the load ZL. Hint: what information do you get from that the slotted line is an air line? 3. A voltage generator with vg(t) = cos(2 109t) V and an internal impedance Zg = 100 is connected to a 100- lossless air-spaced transmission line. The line length is 5 cm and it is terminated in a load with impedance ZL = (200j200) . Find the following: (a) Reflection coefficient at the load, (b) Input impedance Zin at the input end of the transmission line, (c) The input voltage vi(t) and input current ii(t), [Hint: simple circuit. First use phasors, then get to the time domain.] (d) The average input power Pav, [hint: again, simple circuit] (e) The incident voltage phasor V0 , incident current phasor I 0 , and average incident power Pinc, and (f) The reflected voltage phasor V0 , reflected current phasor I 0 , and average reflected power Pref.