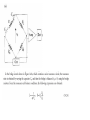
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. dia - Shrek
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
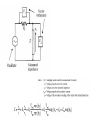
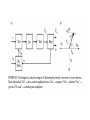
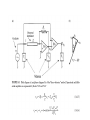
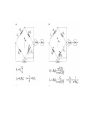
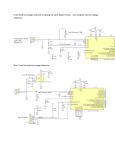
Resistivity - resistance The applied voltage or current can cause heating of the material, which can change its resistivity. Even if heating of the sample is not a problem, Ohm’s law is not always obeyed. A critical check of a four-point measurement is to reverse the leads and remeasure the resistance. The most difficult part of making resistivity measurements is often making good electric contacts to the sample. The measurement system should be calibrated before measuring any material samples. Calibration procedures are usually described in the equipment manuals. The input resistance (or “impedance”) of the voltmeter should be at least 10 0000 higher than the resistance of the sample bar. The input impedance is usually listed in the equipment specifications. Note that some voltmeters and electrometers have a sufficiently high impedance between either of the inputs and ground, but not between the two inputs. In this case, it is necessary to use two voltmeters/electrometers (each with one input connected to ground and the other input connected to the sample bar) Voltage and current comparison Wheatstone bridge Capacitance Inductivity Current and voltage method Bridge - method Resonance - method In the “shunted T” network presented in Figure 14.8b, the state of balance (i.e., the minimal voltage v0 value) is achieved by tuning the multiloop LCR circuit to parallel resonance. The circuit analysis [7] is based on the “stardelta” transformation of the CrRrCr element loop and leads to the relations for L and R values: Up to 100Mhz