* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
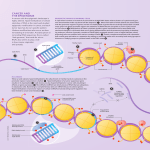
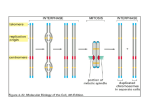
Depiction of some aspects of the chromatin surrounding the CpG sites (open lollipops) in a CpG island in a promoter of a normally unmethylated gene (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (arrow) unmethylated promoter is occupancy by widely spaced nucleosomes composed of histone complexes in which key residues in the tails of histone H3 are in the acetylated state (green ovals) and the tails of histone H3 are methylated at lysine 4. The region is accessible to key components of the gene transcription apparatus including primary transcription factors (TF), proteins with histone acetyltransferase activity (HAT) that maintain the histones in an Source: DNA Methylation and Epigenetic Silencing of Genes in Cancer, The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease acetylated state, and transcriptional coactivators (CoA) that also may have HAT. Flanking regions to either side of the unmethylated CpG island contain Citation: Valle D, regions Beaudetare AL,embedded VogelsteininB,chromatin Kinzler KW, AntonarakisofSE, Ballabio A, Gibson K, Mitchell The Online Metabolic Molecular methylated cytosines. These characteristic transcriptionally silenced regionsG. characterized by bindingand of MBPs to Bases of Inherited Disease; 2014 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 11, 2017 the methylated sites (black circles) and nucleosomes that are more tightly compacted and have deacetylated histones (red ovals). The MBPs are part of Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved complexes that contain©HDACs, which facilitate the deacetylated state of the histones. The apparatus for DNA methylation, the DNA methyltransferases, and their complexes with transcriptional corepressors and HDACs have access to the flanking areas but not to the CpG island promoter region within the