* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Structure and Functions A26-41
Survey
Document related concepts
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
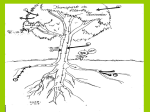
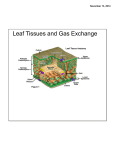
Ch. 2: Plant Structure and Functions Lesson 3 Notes: A26-41 How do a plant’s parts help it survive? (p. A30-31 -roots hold it in ground protecting it from moving by wind or rain -roots take water into plant from soil and store food for plant -taproots: one large root with a few hairy branching roots; grow deep into ground -fibrous roots: made of only thin hairy branching roots (ex. grass or rye plants) -Parts of a root: Xylem- tissue through which water and minerals flow up through plant Cortex- layer just inside epidermis of roots and stems; stores food Epidermis- outermost layer of root, stem, or leaf Root cap- thin covering made up of cells; protects root tip as it grows into soil Phloem- tissue through which food from leaves moves down through plant Cambium- layer that separates xylem from phloem; where new xylem and phloem are made How are stems similar? (p. A32-33) -all stems support plants -all stems hold transportation system for plants (ways to move food and water) -xylem= moves water and minerals up from roots -phloem= moves food from plant’s leaves to other parts -cambium= layer of cells that separates xylem and phloem What are leaves? (p. A34-35) -simple leaves= single leaves (example: maple and oak leaves) -compound leaves= leaves come in clusters/groups (examples: chestnut and locust leaves) -epidermis= outermost layer of leaf -cuticle= waxy coating that keeps water inside leaf -stomata= tiny pores in bottom of leaves that allow air to come inside -guard cells= surround stomata and open and close it -leaves capture sunlight to help plant make its own food -transpiration= when water evaporates from leaves and moves up through plant to replace lost water What is photosynthesis? (p. A36-37) -food making process in plants -sunlight strikes green leaf/ chlorophyll is found inside chloroplasts and makes sugar and oxygen with water and carbon dioxide/ sugars go into leaf’s veins and move throughout the plant -respiration= process of releasing energy plant uses How does water get from roots to leaves? (p. A38-39) 1. water and dissolved minerals enter plant’s root hairs from soil 2. water passes through cortex of root, enters xylem, and travels up stem 3. transpiration up in leaves draws water into xylem of plant’s stem 4. water moves up stem through leaf’s petiole, and into veins; veins carry water to leaf’s cells 5. almost 99% of water is given off into air by transpiration through leaf’s stomata What parts of plants do you eat? (p. A40-41) -roots, stems, leaves, seeds, fruits, flowers, bark, sap (see chart on p. A 40 for examples)