* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LESSON 1 Defining biodiversity
Survey
Document related concepts
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical Andes wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Animal genetic resources for food and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
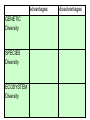
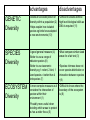
Defining Biodiversity What is the nature and value of biodiversity? Learning Objectives – * To know & understand what biodiversity is * To be able to explain the three ways in which biodiversity can be measured * To be able to use key terminology accurately and confidently Locate the habitat of the following creatures on a world map 1. Fossa 2. Pink River Dolphin 3. Bengal Tiger 6. Sun Bear 4. Tibetan Fox 5. Kakapo 4. 3. 6. 2. 1. 5. Mallomys giant rat • A giant rodent five times the size of a common rat has been discovered in the mountainous jungles of New Guinea. • The 1.4kg Mallomys giant rat is one of two species of mammal thought to be new to science documented on an expedition to an area described as a "lost world". • Conservationists also found a pygmy possum - one of the world's smallest marsupials on the trip to the remote north of Papua province, Indonesia. • 18 December 2007 - BBC The Biodiversity found on Earth today consists of many millions of distinct biological species, which is the product of nearly 3.5 billion years of evolution. Biological diversity means the variability among living organisms from all sources and the ecological complexes of which they are part. This includes diversity, within species, between species and of ecosystems Genetic diversity Species diversity Ecosystem diversity Biodiversity is often used as a measure of the health of biological systems. Genetic diversity is a level of biodiversity that refers to the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. Genetic diversity and Biodiversity are dependent upon each other -- Genetic Diversity within a species is necessary to maintain biodiversity. Genetic diversity plays a very important role in survival and adaptability of a species because when a species’ environment changes, slight gene variations are necessary for it to adapt and survive. A species that has a large degree of genetic diversity among its population will have more variations from which to choose the most fit genes. Species that have very little genetic variation are at a great risk. With very little gene variation within the species, healthy reproduction difficult. http://www.bbc.co.uk/lear ningzone/clips/6244.html Watch the clip, then describe how genetic variation has helped this species to survive and adapt 1. Genetic Variation exists among individuals within giraffes – some have short necks like a horse, others have slightly longer necks. 2. All the giraffes are experiencing competition for resources (food and space) 3. This competition would lead to the death of some individuals (mainly shorter necked ones, as their food is also eaten by all the other short necked animals) while others would survive (the longer necked ones have an advantage as they can reach the juicy leaves at the top!) 4. Individuals that have advantageous variations are more likely to survive and reproduce. Species diversity is an index that incorporates the number of species in an area and also their relative abundance. Simpson's Diversity Index: D = (n / N)2 n = the total number of organisms of a particular species N = the total number of organisms of all species A value of 0 indicates infinite diversity, a value of 1 indicates no diversity Ecosystem diversity refers to the diversity of a place in terms of its variety of ecosystems or habitats i.e what is the diversity of different ecosystems within the UK, as opposed to the diversity of species within these ecosystems. advantages GENETIC Diversity SPECIES Diversity ECOSYSTEM Diversity disadvantages advantages disadvantages GENETIC Diversity •Allows an accurate picture of diversity within a population (2) •Helps explain how isolated species eg birds have adapted to new environments (10) •Difficult to assess without high level biological skills as DNA is required (11) SPECIES Diversity •A good general measure (4) •Better to use a range of indicator species (8) •Better to use taxonomic diversity eg 1 rodent, 2 bird, 1 lizard species = better than 4 bird species (7) •Must compare similar sized areas for a fair test (3) ECOSYSTEM Diversity •A more complex measure as it considers the interaction of species within their environment (1) •Possibly more useful when deciding which areas to protect as has a wider focus (5) •Difficult to know where the boundary of the ecosystem is (6) •Species richness does not cover species distribution or interaction between species •(9) Defining Biodiversity • http://www.daversity code.com/ • What is meant by the ‘web of life’? Watch the clip carefully then draw a diagram to support your answer. Ecosystem Key Words • Dominoes Keep your cards to yourself – if you think you have one that matches a domino that has been laid down then put your hand up and explain!