* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Why Sooo Much Coal?
Survey
Document related concepts
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
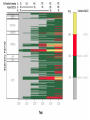
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Coal in China wikipedia , lookup
Fossil fuel phase-out wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
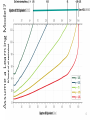
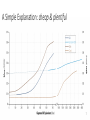
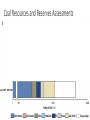
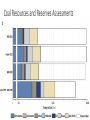
Too Much Coal? Justin Ritchie & Hadi Dowlatabadi Institute for Resources, Environment & Sustainability UBC CEDM Annual Meeting May 2016 0 Representative Conc. Pathways RCP -- ΔT 8.5 – 4.9 °C 6.0 – 3.0 °C 4.5 – 2.4 °C 2.6 – 1.5 °C 1 Cumulative CO2 from Gas, Oil & Coal 2 Background • IAMs of climate change are challenged by how to represent unknown technical change. This has led to exogenously defined technical change delivering: • economic growth • energy efficiency • IAMs also had to deal with how the cost of new supply alternatives would evolve over time. This has led to “learning by doing” models to represent falling costs of new technology: • Renewable resources • Fossil fuel discovery, development & production 3 4 https://www.google.ca/search?q=ford+model+t+factory&safe=off&client=safari&rls=en&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjOmeTqk9_MA hUBwYMKHaC-D-8Q_AUIBygB&biw=1305&bih=816&dpr=2#q=ford+model+t+factory&safe=off&tbm=isch&tbs=isz:l&imgrc=5hwMo2hLP9-8KM%3A Blurred lines Geologic resources too expensive to exploitable Known reserves exploitable at market competitive cost 5 6 Assume a Learning Model? A Simple Explanation: cheap & plentiful 7 Energy Market Shares 1880-2100 8 Coal Energy per Capita 9 Coal Resources and Reserves Assessments 10 Coal Resources and Reserves Assessments 11 Actual learning since 1989 • As we have characterized more of the earth’s crust, we have found more coal deposits. • Even as experience increases, coal is growing more costly to produce. Despite all time high coal prices, Rogner downgraded reserves by ~2/3rd from 1998 to 2014. • That coal share is declining due to: • Economic reasons: of high cost coal cf. low cost gas • Environmental reasons: unrelated to climate change. 12 Total Cumulative Primary Energy AR5 13 Total Cumulative Primary Energy AR5 14 Total Cumulative Primary Energy AR5 15 Summary • Fossil fuel reserves have been characterized using a Learning by Extraction model in all* climate change IAMs. • The models have not kept up with assessments. • The LBE models bias fossil energy prices downward and availability/use upward. • RCP 6.0 is likely characteristic of an upper bound 16 Summary • Fossil fuel reserves have been characterized using a Learning by Extraction model in all* climate change IAMs. • The models have not kept up with assessments. • The LBE models bias fossil energy prices downward and availability/use upward. • RCP 6.0 is likely characteristic of an upper bound Mitigation targets are likely to be less daunting and shadow carbon prices lower than assessed in IAMs using IPCC family of scenarios. 17 Too much coal, yes. But are there enough cow bells? http://www.france-voyage.com/francia-foto/muccha-razza-montbeliarde-1416.htm 18 19 20 How Much Coal is There? Cumulative CO2 from Gas, Oil & Coal 21