* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Yoruba Language
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Junction Grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
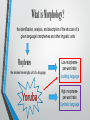
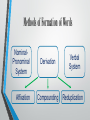
Yoruba Language What is Morphology? the identification, analysis, and description of the structure of a given language's morphemes and other linguistic units Morphemes the smallest meaningful unit of a language Low morphemeper-word ratio Isolating language High morphemeper-word ratio Synthetic language Yoruba People An ethnic group of southwestern Nigeria and southern Benin in West Africa Yoruba Language a Nigerian language spoken in West Africa, mainly in Nigeria Why is Yoruba an Isolating Language? Low morpheme-per-word ratio / Subject-verb-object A single or compound word gives a complete sentence Ó rá (He disappears) antidisestablishmentarianism "against-ending-institutionalize-condition-advocate-ideology" "the movement to prevent revoking the Church of England's status as the official church" Methods of Formation of Words NominalPronominal System Affixation Derivation Compounding Verbal System Reduplication Affixation Nominal forms can derive from verbs and verb phrases by means of affixes Prefixes a- and ò- are used to form agent nouns Example: denoting a person or an object that performs an action apẹja: fisherman (pa = kill, ẹja = fish) òjíṣẹ́: messenger (jẹ́ = answer, iṣẹ́ = message) Prefixes ì- and à- are used to form abstract nouns from verbs and verb phrases ìṣẹ́: poverty (ṣẹ́ = to break) àlọ: going (lọ = go) Reduplication • Used to express intensification • To form agentive nouns and adjectives from verbs, verbal phrases and ideophones Intensive = púpọ̀ (much) → púpọ̀púpọ̀ (very much) Adjective = jẹ (to eat) → jíjẹ (edible) Agentive noun = jà (fight) + ogun (war) → jagunjagun (warrior) Ideophone = ramúramù (a loud noise) Compounding Two nouns are joined together by deleting the initial vowel of the second word to create a new word with a different meaning ewé (leaf) + ọbẹ̀ (soup) = ewébẹ̀ (vegetable) ìyá (mother) + ọkọ (husband) = ìyakọ (mother in law) ẹran (meat) + oko (farm) = ẹranko (animal)