* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Crusades! - Travel History
Survey
Document related concepts
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Arsuf wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Military history of the Crusader states wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
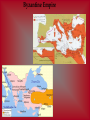
The Crusades Christian Holy War Copyright © Clara Kim 2007. All rights reserved. Religious War • JIHAD – Three types of struggles • an internal struggle to maintain faith, • the struggle to improve the Muslim society • the struggle in a holy war. • CRUSADE – capitalized : any of the military expeditions undertaken by Christian powers in the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries to win the Holy Land from the Muslims – a remedial enterprise undertaken with zeal and enthusiasm The Invaders • In 1093, Byzantine Emperor named Alexius Comnenus ask for help against invaders – THE INVADERS: The Muslim Turks aka Seljuk Turks • The Muslim Turks were trying to take over the Byzantine capital of CONSTANTINOPLE Byzantine Empire Pope Urban II •Pope Urban II read the letter asking for help and called for a “holy war” or Crusade •He said those who fought and died in the Crusades would be promised a spot in Heaven with all sins forgiven THE GOAL •The goal of these Christian soldiers were to recover – 1. Jerusalem and – 2. Holy Land •They wanted it back from the Muslim Turks Jerusalem • Holy center shared by three major world religions • Christianity-Jesus was crucified there • Islam-Mohammed’s journey to Heaven took place there • Jews- Abraham built the original holy temple there • Kicked out of Jerusalem until 1947 and the founding of modern Israel Crusader Spirit • There were economic and religious motives for the Crusades – Kings and the Church: A way to get rid of knights who always fought each other and threatened the peace of the kingdom – Younger Sons: A way to gain land and position in society since the oldest son gets everything – Knights and Commoners: fired by religious zeal (passion) Peter the Hermit preacher in Germany rallied thousands to his banner including: a few German knights Turned “army” loose on Jews living on the Rhine River Marched to Byzantium and destroyed the countryside “army” destroyed by Turks after leaving safety of Byzantium. First Crusade • Pope Urban recruited from French nobility • Unprepared troops • Carved in up into 4 Crusader states • Captured Jerusalem and • No strategy massacred inhabitants for 7 • Four crusader leaders days made uneasy alliance Map of Crusader States • Completely surrounded by Muslim nations. • Loss of Edessa starts 2nd Crusade Second Crusade • Muslim leader Saladin destroys Crusader States armies at Battle of Hattin • takes control of Jerusalem • Muslim Turks re-conquer the city • Starts 3rd Crusade • Saladin is described to be honest and brave Third Crusade • The “Kings Crusade • Richard the Lion Hearted English King, Frederick Barbarossa of the Holy Roman Empire, and Philip II of France march to Holy Land • Barbarossa drowns and German army returns home • Philip II and Richard argue over who should rule Jerusalem • recapture Acre • Richard defeats Saladin at every battle – Signs uneasy alliance with Saladin • Richard and Saladin respected each other Fourth Crusade • New call for Crusade against the Turks • Venice: Byzantium’s vassal state • Persuades Crusaders that Byzantium deserves to fall • Break into city and create the Latin Empire – Stole much of Byzantium’s wealth – Repeatedly fail to make peace with Byzantium’s neighbors: Turks, Bulgaria, Trebizond, and Nicea. In the End •The Christians are finally pushed out of the Holy Land •Muslim Turks are the victors and take over the Byzantine Empire in 1453 Economics Venice and Genoa Cities based on trade and have large navies Made fortunes off of transporting Crusaders eastward Opened trade with the East: lost Greek and Roman texts, silk, spices, etc. Effects of the Crusades • Negatives: – Weakened the Byzantine Empire, the Pope and nobles – Kings become stronger – Leaves a legacy of bitterness between the Christians, Jews and the Muslims • Positives: – Stimulated trade and spread of technology throughout the Mediterranean and Middle East