* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complex Lipids
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
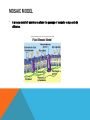
STRUCTURES • Triglycerides are significant components of fat storage cells. • Complex lipids are important because they constitute the main components of membranes. CLASSIFIED IN 2 GROUPS • Phospholipids – contain an alcohol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group. • Two types • Glycerophospholipids- alcohol is a glycerol. • Sphengolipids – alcohol is sphingosine. CONT’D • Glycolipids – complex lipids that contain carbohydrates. ROLES • Complex lipids form the membranes around body cells and around small structures inside the cells. • These are called Organelles. • Unsaturated fatty acids are important components of these lipids. • Most lipids contain at least one unsaturated fatty acids. CELL MEMBRANES • Cell membranes separate cells from the environment and provide transport for nutrients and waste products into and out of cells. • These membranes are called – Lipid Bilayers. LIPID BILAYERS • The arrangement of lipid bilayers leaves the hydrophilic heads projecting to the inner and outer surfaces of the membranes. • The unsaturated fatty acids prevent the tight packing of the hydrophobic chains in the lipid bilayer, providing a liquid-like character to the membranes. • Effect is similar to the one that causes unsaturated fatty acids to have lower melting points than saturated fatty acids. LIPIDS CONT’D • The lipid part of the membrane serves as a barrier against any movement of ions or polar compounds into and out of the cells. MOSAIC MODEL • A mosaic model of membranes allows the passage of nonpolar compounds by diffusion. WHAT ARE GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS? • Very similar to fats • Membrane components of cells throughout the body • The alcohol is glycerol • If the alcohol is chlorine, a quaternary ammonium compound, the glycerophospholipids are called phosphatidyl – cholines • Common name is – Lecithin LECITHIN • The typical lecithin molecule has stearic acid on one end and linoleic acid in the middle. • Lecithin is a major component in egg yolk • Includes both polar and nonpolar portions within one molecule. • Excellent emulsifier • Used in mayonnaise as well. • Lecithin is a negatively charged phosphate group and a positively charged nitrogen from the choline. • Lecithin is only one example of glycerophospholipids. CEPHALINS • Similar to lecithins in every way except that, instead of choline, they contain alcohols, such as ethanolamine, or serine. PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOLS (PI) • Another important group is phosphatidylinositols or (PI). • Alcohol inositol is bonded to the rest of the molecule by a phosphate ester bond. WHAT ARE SPHINGOLIPIDS? • Myelin → Coating of the nerve axons, contains a different kinds of complex lipid. • Sphingolipids → alcohol portion is sphingosine. • Not randomly distributed in membranes. CERAMIDE • The combination of a fatty acid and sphingosine is called the ceramide portion of the molecule, because many of these compounds are also found in cerebrosides. • The ceramide part of complex lipids may contain different fatty acids. SPHINGOMYELIN • Sphingomyelin → most important lipids in the myelin sheaths of nerve cells and are associated with diseases such as multiple sclerosis. WHAT ARE GLYCOLIPIDS? • Complex lipids that contain carbohydrates and ceramides. TYPES OF GLYCOLIPIDS • Cerebrosides – consists of ceramide, and mono or oligosaccharides. • In cerebrosides the fatty acid of the ceramide part may contain either 18 carbon or 24 carbon chains. • Gangliosides – Contain a more complex carbohydrate structure. • The latter form is only found in these complex lipids*