* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - singhscience
Survey
Document related concepts
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
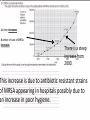
Core Biology Smart Teach 5: Disease and Immune System Key terms used in exam questions • Pathogen – An microorganism that causes an infectious disease. • Antibiotic – A chemical that kills bacteria. • Antiseptic – A chemical that is used externally to prevent the spread of pathogens. • Resistant – Used in this context it usually refers to when bacteria are no longer killed by an antibiotic. What are the four pathogen types you are most likely to be asked about? • • • • Bacteria – Causes cholera/dysentery. Viruses – Causes influenza(‘flu)/common cold. Fungi – Causes Athlete’s Foot Protozoa – Causes malaria • You also need to be able to give examples of how they are spread through populations. The next few slides will give the key information for each method and an example for each. • Airborne – Spread through the air eg colds, influenza, Tuberculosis. • Waterborne – Drinking infected water eg cholera. • Food – Eating infected food eg Salmonella (Food poisoning) • Skin-to-skin contact – Touching an infected person, or walking where they have eg athlete’s foot and verucas are spread quite commonly in swimming pools. • Body fluids – Either through infected blood or having unprotected sex eg HIV. • Vectors – Carriers of pathogens eg mosquitoes carry the protozoa that causes malaria, houseflies carry the bacteria that causes dysentery. It is the mosquitoes and the houseflies that are the vectors. What defences does our body have? Mucus Lysozymes in tears and saliva Cilia Skin Hydrochloric acid in the stomach Chemical vs Physical The chemical defences are: Hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Lysozymes in the tears and saliva. You could be asked to give an example of either chemical or physical defences. The physical defences are: Skin. Cilia. Mucus. Antibiotics vs. Antiseptics Antibiotics – You could be These are given data chemicals to in the form kill bacteria of a graph only. or table to evaluate the use of these Antiseptics – These are chemicals to kill pathogens outside of the body eg handwash, wipes etc. Antibiotic resistance • Over use of antibiotics can lead to them becoming resistant to antibiotics eg the antibiotics will no longer work. • Resistance is usually due to a genetic mutation. • MRSA has caused problems in hospitals because some strains have become resistant to antibiotics. • You should always finish a course of antibiotics even if you feel better so that all the bacteria are killed and don’t have a chance to become resistant. • Doctors will no longer prescribe antibiotics all the time now, they are more selective. MRSA questions usually involve graphs • The next slide will take you through a typical exam question. As time increases Number of case of MRSA increases There is a steep increase from 2000. This increase is due to antibiotic resistant strains of MRSA appearing in hospitals possibly due to an increase in poor hygiene. Now lets have a look at some exam questions about this.......... Answer Question Number (b) Acceptable answers Mark B (1)