* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Community Ecology Ecosystems and the Biosphere
Survey
Document related concepts
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Arctic ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Old-growth forest wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
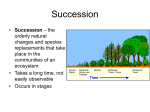
Unit 2 Species Interactions, Succession and Biomes Chp 4 A community has many interacting species. These interactions are called symbioses. • • • • • • • Predator-prey ( + , -) Mimicry (copycat) Plant-herbivore (form of predation) Parasitism (Ecto and Endo parasites) Competition Mutualism ( + , +) Commensalism ( +, 0 ) Succession • Fires, Floods, Landslides, Hurricanes, and Volcanic eruptions can cause ecological succession • Over time the life changes in stages. • Primary succession= area that has NOT supported life(bare rock or sand dune). • Secondary succession= replacement of species over time following a disruption. • Pioneer species are the first to develop. Climax Community • A stable end point of succession is called a Climax Community. • This remains constant for long periods of time. Terrestrial Ecosystems BIOMES= are very large terrestrial ecosystems that contain a number of smaller but related ecosystems within them. There are seven major biomes characterized by significant plant and animal life, climate, rainfall,etc. Biomes • • • • • TUNDRA Cold and treeless Largest and northernmost biome Permafrost=permanently frozen layer of soil. Little rain, short growing season Grasses,mosses,caribou,snowy owls, arctic foxes, and snowshoe hares Taiga • • • • • Forest, cone-bearing trees, firs, hemlocks Long and cold winters Short summers Low-nutrient soil Moose, Bears, Wolves, most hibrenate 6-8 months of the year. Temperate Deciduous Forest • • • • Tress that lose their leaves in the fall Even precipitation through the seasons Birch, Elm, Oak, and Willow trees Deer, Fox, Raccoon, Squirrell Temperate Grassland • • • • Little rainfall Rich fertile soil Large herds of grazing animals Much of the area is used for growing crops • Deserts • Less than 9.9inches of rain per year • Hot days and cold nights • Animals and plants have adaptations to conserve water • Cacti, Lizards, Snakes Savannas • Tropical or subtropical grasslands with scattered trees and shrubs • Support many herbivores=zebras, giraffes, gazelles • Periods of drought alternate with periods of rain Tropical Rain Forest • Very tall trees • Abundant rainfall • Canopy is high tree tops that shade the forest floor • Epiphytes live on these tall tress (but not parasites) • Contain the most species, most diverse