* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Byzantine, Islamic and Middle Ages Key Events
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic terrorism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Imamate (Twelver doctrine) wikipedia , lookup
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islamic monuments in Kosovo wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Liberalism and progressivism within Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islamic influences on Western art wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
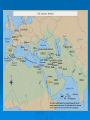
Islamic World Islamic Era - Chronology 570 CE – Birth of Muhammed, founder of Islam 610 CE – Muhammed’s vision that creates Islam (Archangel Gabriel comes to him) 622 CE – Muhammed leaves Mecca for Medina and begins gaining converts – this event is known as the Hegira (Hajj) 630 CE – Muhammed and followers return to Mecca and overtakes the city – the Kabah is set up as major Islamic shrine 632 CE – Death of Muhammed, his father-in-law Abu – Bakhr takes over and creates the title caliph; begins the creation of an empire of Islam by conquering neighboring lands. At Abu-Bakhr’s death Umar takes over as caliph. Muslims divide into many subgroups. Islamic Era - Chronology 718 CE – Spain is under Muslim control 734 CE – Battle of Poitiers – Muslim spread is stopped by Charles Martel of France 762 – 766 CE – The Abbasid Dynasty takes over from Umayyads (except in Spain) and move capital from Damascus to Baghdad 788 – 879 CE – Several countries break free from caliphate and set up individual kingdoms and dynasties 879 CE – Seljuk Turks begin conquest of Mesopotamia and Persia 900 CE – Fatimids take over in Egypt and conquer all of North Africa Islamic Era - Chronology 945 CE – Abbasid power falls to the Shiites 969 – 1171 CE – Fatimid Dynasty recreates a smaller version of the Caliphate in Egypt 1037 – 1194 CE – Seljuk Turk Dynasty 1077 CE – Seljuk Turks conquer most of Arabia, Palestine, Syria, Lebanon 1099 CE – Crusades begun against Muslims in the Holy Land by Pope Urban 1187 CE – Saladin ends Western control of Holy Land (Outremer) after Battle of Hattin Islamic Era - Chronology 1248 CE – Muslims lose control of most of Spain except area around Granada 1251 CE – Malmuk Dynasty takes over caliphate in Egypt 1258 CE – Abbasid Dynasty is completely wiped out by Mongol invasion 1327 CE – Seljuk Empire collapses; Arab world splits into several kingdoms 1453 CE – Ottoman Empire defeats the Byzantine Empire; move capital to Istanbul (Constantinople) 1492 CE – Muslims completely expelled from Spain 5 Pillars of Faith – (Sunni) 1) Shahadah – profession of faith – “There is no God but Allah, and Muhammad is his messenger” 2) Salah – ritual prayer done 5x a day at dawn, noon, mid-afternoon, sunset and evening 3) Zakat – giving to the poor – everyone must give something depending on what they earn 4) Sawm – fasting during month of Ramadan – refraining from food, drink and sexual intercourse from dawn to dusk each day of the month – also supposed to get along with others better and get closer to Allah during this time (there are exceptions for health, etc.) 5) Hajj – pilgrimage to Mecca – every able bodied Muslim must make the pilgrimage at least once in their lifetime – must walk around the Kaaba 7 times, touch the stone and symbolically throw rocks at the devil In Shiite Islam there are the additional pillars of Jihad (personal struggle against Islam’s enemies) and Khum (giving a tithe to the Imam) Additional Component Jihad- Important concept in both Sunni and Shia Islam, signifies a struggle. Two types, the struggle within (which the Qu’ran deals mainly with), and the struggle (wars of religion) without. Shia consider the inner Jihad an essential element of the faith. Jihad is often misused in terminology and in its purpose. Terrorist group Al-Qaida is a Sunni organization. Sufism Sufism, the mystical tradition of Islam, dates back to Muhammad’s lifetime Forms of Sufism are found in both Sunni and Shi’a Islam Sufism has often stood in contrast to more legalistically oriented approaches to Islamic life, to the extent that some orthodox Sunnis do not consider Sufis to be Muslim http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9gnWxiy44fA – Urdu Sufi Song http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L_CfZxDfZA&feature=related - Dervishes Other Branches of Islam (Wahabi) – sect in 1700s that believed any forms of Islam after the 900s were wrong and need to be expunged, led to many jihad’s against the Sunni’s in particular. Against ostentation so no minarets on mosques and only plain clothing allowed An orthodox, traditionalist branch Wahhabi Other branches of Islam Ismailis – form of Shia, accepts 12 Imams, split on 6th Imam and succession Druze – offshoot of Ismaili sect, that promotes gnostic philosophy, they believe the Fatimid Caliph will return on Judgment Day as the Mahdi Ahmadiyya – founded in 1889, claim Mahdi came and his descendants are the caliphs in India Hashashin – “Assassins;” an order of Ismailis that were trained killers meant to harass the Sunnis and others whom they considered heretics; rumors of the use of hashish to prepare them for their suicide missions and the promises of direct passage to heaven with wine and women Other branches of Islam Kharijite – only surviving sect is the Ibadi; claim the Imam must be pure spiritually and stand fast in their faith; some Imams not accepted Ahl-e Haqq – believe that god continuously manifests himself in reincarnations throughout time; world is divided into 2 – internal and external Mahdavism – monastic version of Islam; focus on prayer and meditation Moorish Science – founded in 1913 in America; claims all African Americans are originally Moors and therefore should be Muslim Nation of Islam – founded in Detroit in 1930; believes Fard Muhammad was God on earth; “taking back the true place of the black man and woman;” considered heretical by most other Muslims Other Branches of Islam Babs/Baha’i – followers of Shiraz, who claimed to be Mahdi (Messiah) and changed his name to “The Bab”; broke away from mainstream Islam, and was executed in Iran in 1850; teaches humanity is one single race all coming from God Sikhs – combination of Islam and Hinduism that rejects both religions policies of discrimination; equality of all humans Nuwaubu – originally a sect of Islam; now more of a New Age cult, believes extraterrestrial beings speak through their founder Malachi York and reveal God’s plan; use ancient Egyptian and Sumerian texts to prove it. A famous law from the Quran 5.38. As to the thief, Male or female, cut off his or her hands: a punishment by way of example, from Allah, for their crime: and Allah is Exalted in power. On Women Sura 4:3 says: “ And if you be apprehensive that you will not be able to do justice to the orphans, you may marry two or three or four women whom you choose. But if you apprehend that you might not be able to do justice to them, then marry only one wife, or marry those who have fallen in your possession.” Sura 4:34 says “Men are the protectors and maintainers of women, because Allah has given the one more (strength) than the other, and because they support them from their means. Therefore the righteous women are devoutly obedient, and guard in (the husband's) absence what Allah would have them guard. As to those women on whose part ye fear disloyalty and ill-conduct, admonish them (first), (Next), refuse to share their beds, (And last) beat them (lightly); but if they return to obedience, seek not against them Means (of annoyance): For Allah is Most High, great (above you all)“ On suicide and killing “And do not kill yourselves, God is merciful with you. And whosoever does that (kills self) with aggression and inequity, we will make them suffer in Hell fire, and this is easy for God to do” (29-30, 4). “He who kills a person without (the latter) having killed another person, it is as if he has killed all of humanity, and he who makes one person survive, it is as if he has caused all humanity to survive” (32,5) "The person who participates in (Holy battles) in Allah's cause and nothing compels him to do so except belief in Allah and His Apostles, will be recompensed by Allah either with a reward, or booty (if he survives) or will be admitted to Paradise (if he is killed in the battle as a martyr). Had I not found it difficult for my followers, then I would not remain behind any sariya going for Jihad and I would have loved to be martyred in Allah's cause and then made alive, and then martyred and then made alive, and then again martyred in His cause." Whoever purposely throws himself from a mountain and kills himself, will be in the (Hell) Fire falling down into it and abiding therein perpetually forever; and whoever drinks poison and kills himself with it, he will be carrying his poison in his hand and drinking it in the (Hell) Fire wherein he will abide eternally forever; and whoever kills himself with an iron weapon, will be carrying that weapon in his hand and stabbing his abdomen with it in the (Hell) Fire wherein he will abide eternally forever." The Quran on Christians and Jews 5.51. O ye who believe! take not the Jews and the Christians for your friends and protectors: They are but friends and protectors to each other. And he amongst you that turns to them (for friendship) is of them. Verily Allah guideth not a people unjust. 5.57. O ye who believe! take not for friends and protectors those who take your religion for a mockery or sport,whether among those who received the Scripture before you, or among those who reject Faith; but fear ye Allah, if ye have faith (indeed). 5.60. Say: "Shall I point out to you something much worse than this, (as judged) by the treatment it received from Allah. those [people of the Book (Jews and Christians)] who incurred the curse of Allah and His wrath, those of whom some He transformed into apes and swine, those who worshipped evil;- these are (many times) worse in rank, and far more astray from the even path!" 5.64. The Jews say: "(Allah)'s hand is tied up." Be their hands tied up and be they accursed for the (blasphemy) they utter. Nay, both His hands are widely outstretched: He giveth and spendeth (of His bounty) as He pleaseth. But the revelation that cometh to thee from Allah increaseth in most of them their obstinate rebellion and blasphemy. Amongst them we have placed enmity and hatred till the Day of Judgment. Every time they kindle the fire of war, Allah doth extinguish it; but they (ever) strive to do mischief on earth. And Allah loveth not those who do mischief. 5.69. Those who believe (in the Qur'an), those who follow the Jewish (scriptures), and the Sabians and the Christians,- any who believe in Allah and the Last Day, and work righteousness,- on them shall be no fear, nor shall they grieve. 5.72. They do blaspheme who say: "(Allah) is Christ the son of Mary." But said Christ: "O Children of Israel! worship Allah, my Lord and your Lord." Whoever joins other gods with Allah,- Allah will forbid him the garden, and the Fire will be his abode. There will for the wrong-doers be no one to help. 5.73. They do blaspheme who say: Allah is one of three in a Trinity: for there is no god except One Allah. If they desist not from their word (of blasphemy), verily a grievous penalty will befall the blasphemers among them. 5.74. Why turn they not to Allah, and seek His forgiveness? For Allah is Oft- forgiving, Most Merciful. 5.75. Christ the son of Mary was no more than an apostle; many were the apostles that passed away before him. His mother was a woman of truth. They had both to eat their (daily) food. See how Allah doth make His signs clear to them; yet see in what ways they are deluded away from the truth! 5.82. Strongest among men in enmity to the believers wilt thou find the Jews and Pagans; and nearest among them in love to the believers wilt thou find those who say, "We are Christians": because amongst these are men devoted to learning and men who have renounced the world, and they are not arrogant. The Virgin Myth The Quran never mentions 72 virgins (it is in a Hadith (Islamic traditional writings) The virgins mentioned in the Quran are for all Muslims, not just martyrs "Dark-eyed virgins sheltered in their tents (which of your Lord's blessings would you deny?) whom neither man nor jinnee will have touched before." "The Prophet Muhammad was heard saying: 'The smallest reward for the people of paradise is an abode where there are 80,000 servants and 72 wives, over which stands a dome decorated with pearls, aquamarine, and ruby, as wide as the distance from Al-Jabiyyah [a Damascus suburb] to Sana'a [Yemen]'." The word “hur” or Al-hur” can be translated in many ways, as hand maidens (female servants); dark eyed virgins; voluptuous women or “white pure raisins” and according to scholars, the use in the Hadith was meant for raisins…. Islamic Terms Islam – submission to Allah (god) Muslim – one who submits to the will of Allah Hajj – pilgrimage to Mecca Imam – religious leader Quran (Koran) – Muslim Holy Book Sura – chapter in the Quran Hegira (hajira) – the trip from Mecca to Medina Qiyama – Day of Judgment Jannah - heaven Islamic Art Characteristics Geometric Patterns No icons, rare animals Heavy use of plasterwork Quotations from Koran used as art – calligraphy Plain interiors Water is used as a way to show off wealth Islamic Art Dome of the Rock 680 - 692 CE Jerusalem, Israel Earliest major Islamic building Jerusalem is 3rd holiest city to Muslims Islamic Art Interior of Dome of the Rock 690 CE Jerusalem, Israel Interior is heavily decorated for an Islamic building The rock in the center marks the alleged place where Abraham was going to sacrifice his first born son; it is also the alleged place where Muhammed was taken by Gabriel on a mi’raj (spiritual journey) to visit heaven and hell Islamic Art – Dome of the Rock Great Mosque Damascus, Syria 706-715 Islamic. The Great Mosque of Damascus, Syria. Courtyard. 706-15. Islamic. Great Mosque of Damascus, Syria. Detail: Mosaic decoration. 715. Islamic Art Cordoba Mosque 786 Cordoba, Spain Begun by Abd-al Rahman Umayyad Dynasty in Spain’s influence is seen here It is considered a masterpiece of Islamic architecture Islamic Art Interior of La Mezquita (Great Mosque of Cordoba) 8th – 10th C. CE Cordoba, Spain Typical Arab style hypostyle hall Horseshoe arcades decorate interior making this one of the most beautiful mosques in the world Dome in front of the mihrab of the Great Mosque Córdoba, Spain 961-965 Islamic Art Mosque of Sulayman II 1550 – 1557 CE Istanbul, Turkey Artist: Sinan This is an enormous Ottoman imperial mosque – to compete with Christian churches in the area Has courtyard with central fountain Islamic Art Interior Mosque of Sulayman 1550- 1557 Istanbul, Turkey Artist: Sinan Vast open space created by domes Limited decoration as Islamic law prohibits idols and idolatry Islamic Art Interior Mosque of Sulayman II 1550 – 1557 CE Istanbul, Turkey Sinan The dome is supported by 8 piers It is over 197 ft high The structural components are the focus rather than being hidden Malwiya minaret of the Great Mosque Samarra, Iraq ca. 848-852 When rediscovered by Western archaeologists they believed it to be the Tower of Babel in error Malwiya minaret and Great Mosque Samarra, Iraq ca. 848-852 Islamic Art Court of the Lions 14th century CE Granada, Spain Located on the grounds of the Alhambra The Nasrid Dynasty built this to show wealth with the use of water Muqarnas dome, hall of the Two Sisters Alahambra Palace Granada, Spain 1354-1391 Mausoleum of the Samanids Bukhara, Uzbekistan early 10th century Despite Islamic prohibitions about extravagant burials – the Samanid rulers built great monuments to death Madrasa-mosque-mausoleum complex of Sultan Hasan Cairo, Egypt 1356-1363 Considered best of its kind Qibla wall, main iwan Madrasa-mosque-mausoleum complex of Sultan Hasan Cairo, Egypt 1356-1363 Qibla wall helps point faithful in right direction for prayer in any mosque Islamic Art Shah-namah book page 1562 – 1583 Persia (Iran) Book was written by Firdawsi It is a work of 60,000 couplets Courtyard of the Great Mosque Isfahan, Iran 11th to 17th centuries Dome of the Shah Mosque Isfahan, Iran 1611-1638 Islamic Art Kaaba Traditional dating c. 2000 BCE, rebuilt 620-630 CE Mecca, Saudi Arabia Holiest spot in the world to Muslims Black stone inside Islamic. The Kaaba, center of the Haram Mosque, Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Last rebuilt 1631. Kaaba Islamic. Muhammad Placing the Black Stone on His Cloak, from Rashid al-Din’s Jami al-Tawarikh (Universal History), copied and illustrated at Tabriz, Iran. 1315. 5-1/8" × 10-1/4". Islamic Art Al Masjid Al Nabawi 7th-13th centuries CE Medina, Saudi Arabia Tomb of Mohammed can be found under the green dome AKA – Dome of the Prophet Originally his house Map: The Trans-Saharan trade routes, ca. 1350. Eastern façade of Friday Mosque Djenne, Mali 13th century, rebuilt 1906-07 Islamic Art Islamic Art Creating a culture of fear http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ib9rofX Ql6w – 3 Things About Islam http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fHlb5FB 26Lo&NR=1&feature=fvwp – Islam World Takeover http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SxpZDl vtOm8&feature=bf_prev&list=PLA03BD1C 50DB50487&lf=results_main – Mr Deity and Matter Islamic Art The end . . . Next lecture . . . Indian Civilization