* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Islam and the Spread of Allah
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
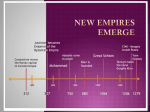
Islam, the Quran, and the Five Pillars Origins of Islam The revelations of The Prophet Muhammad form the basis of the Islamic religion, a monotheistic faith. • WHO? The Prophet (Muhammad) • WHERE? Mecca & Medina (early Muslim cities) on the Arabian Peninsula • HOW? Ideas and travel related to the Ka’aba Beliefs, Traditions, and Customs • Allah – Arabic word for “God” • Qur'an (Koran) – Arabic for “word of God” / holy book • Accepts Judeo-Christian prophets like Moses & Jesus • Five Pillars of Islam • Islamic traditions and customs developed over centuries and created a distinct Muslim culture. Five Pillars of Islam •Creed (Shahada) statement of faith •Prayer (Salat) 5 times/day; facing Mecca •Alms/charity (Zakat) giving to the poor •Fasting (Sawm) abstaining from food/drink •Hajj (Hajj) holy trip to Mecca Islamic Creed • There is only one Allah • Allah rules the whole universe • Idolatry and worshipping other deities is wicked • Allah will bring judgment to the world Geographic Influences Geographic influences on the origin and spread of Islam • Spread along trade routes from Mecca and Medina (diffusion) • Expanded despite great distances: – Crossed deserts and mountains • Spread into Fertile Crescent, Iran, and Central Asia, facilitated by weak Byzantine and Persian empires Influence of geography on economic, political, and social development • Political unity of the first Muslim empire was short-lived • Arabic language spread with Islam and facilitated trade across Islamic lands • Arabic language also stimulated intellectual activity • Slavery not based on race • Harsh Arabian conditions produced fierce loyalty to family Historical Turning Points Major historical turning points marked the spread and influence of Islamic civilization. 1. Death of Ali: Sunni vs. Shi’a division 2. Muslim conquest of Jerusalem & Damascus during the Crusades 3. Islamic capital moved to Baghdad 4. Muslims defeated at the Battle of Tours (France in 732 A.D.) 5. Fall of Baghdad to the Mongols Sects of Islam The Sunni and Shi’a (Shiites) Shi’a (Shiite) (followers of Ali, Sunni Muhammad’s son-in-law) •Approximately 10% of Muslims •Think Muhammad’s successor should be his relatives •Believed in an intermediary called an Imam •Those with religious authority should rule government too • Approximately 90% of Muslims • Believed successors to Muhammad should be chosen by the community • Do not believe in intermediary (middle-man) between Allah and people Successors of Muhammad • Abu Bakr is chosen as Caliph – Bakr’s advisor becomes caliph later. • To avoid civil wars of succession, each diverted attention by invading neighboring, non-Muslim nations. • Weak Persian and Byzantine empires made conquest easy. Muhammad’s Successors Rightly Guided Caliphs •Abu-Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali (caliphate) •Used military force to reestablish Muslim authority after Muhammad’s death •Other caliphs continued to conquer lands with a highly experienced and mobile fighting force Reasons for Success •Muslims drew energy from Islam and fought hard •Armies were well disciplined and had expert leadership •Weakness of the Byzantine and Persian Empires •Those persecuted for other religions welcomed Muslims as liberators •Muslims allowed for Christians and Jews to continue their faith (people of the book) The Umayyads 661 -750 AD/CE •Uthman and Ali were assassinated, a power struggle ensued •Umayyads came to power, moved the capital to Damascus •Focused on wealth rather than simplicity like the Caliphates •Caused a split in the Muslim world (Sunni-Shi’a) The Abbassids 750-1258 AD/CE •Overthrew the Umayyads in 750 AD/CE • Executed all of the Umayyads at a dinner •Moved capital from Damascus (Syria) to Baghdad (Iraq) •Ruled an immense empire by establishing a bureaucracy, trade routes, and banking systems Relationship to Judaism and Christianity • Allah is the same God as that of the Jews and Christians • Jesus is a prophet of Allah but not the Son of God • The Bible, Torah, and Qur’an all contain the word of God but the Qur’an is the perfect version • All believe in a Heaven and Hell, Judgement Day, and they are descendants of Abraham الى Islamic Contributions •Early Islamic civilization was characterized by achievements in science and the arts that transformed the Islamic world and contributed to world civilization. • Architecture: Dome of the Rock (Jerusalem) • Mosaics • Arabic alphabet - Translation of ancient texts into Arabic • Universities Science and Math Urban Life o Arabic numerals (adapted from India), includes 0 o Algebra o Medicine o Geographic Maps o Cities like Baghdad o Home to learning centers o Linked to other cities by trade Muslim Culture Arts and Literature o Mosaics o Koran o One Thousand and One Arabian Nights Society o Tolerant of Christians and Jews One Thousand and One Arabian Nights •A king kills every wife the next morning after their wedding night. Shahrazad cleverly tells 1,001 stories every night in order to save her life •The ideal that Shahrazad has influenced a man of such power in a male dominated society, such as the Middle East, is one even modern day women hold onto. Islamic Contributions in Science • Arabic numerals (adapted from India), includes 0 • Algebra • Medicine • Expansion of geographic knowledge = maps •Astrolabe – measure the angles of the sun and stars Contributions • Art – Features mostly plants and calligraphy – Only Allah should be able to produce the human form • Astronomy – Studied the starts to find the exact location of Mecca and to figure out the correct times to pray – Astrolabe Scholarship • Muslim’s greatest contribution to Western civilizations was preserving and advancing knowledge • House of Wisdom in Baghdad contained books from all over the world • Jewish and Muslim scholars worked together to translate many subjects Dome of the Rock Kaaba in Mecca Mosaic 123456789 0 Arabic numerals Medicine Universities Arabian desert Islam, the Quran, and the Five Pillars