* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KINETICS OF ELIMINATION
Survey
Document related concepts
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Compounding wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Plateau principle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
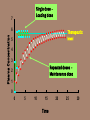
KINETICS OF ELIMINATION SIVANAGESWARARAO MEKALA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPT OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY The four most important parameters governing drug disposition are : clearance volume of distribution half-life bioavailability Clearance (CL): The clearance of a drug is the theoretical volume of plasma from which the drug is completely removed in unit time. Clearance (CL) = __Rate of elimination___ Plasma conc. of the drug When clearance is constant, the rate of drug elimination is directly proportional to drug concentration. KINETICS OF ELIMINATION: Zero order First order FIRST ORDER KINETICS: For most drugs, clearance is constant over the concentration range encountered in clinical settings, and the rate of drug elimination is directly proportional to concentration This is referred to as first-order elimination. Here a constant fraction of drug present in the body is eliminated in unit time The t1/2 of the drugs will always remain constant Half life of a drug following first order kinetics would remain constant irrespective of dose For first order kinetics, Clearance is calculated from the dose divided by the AUC CL = Dose AUC ZERO ORDER OR CAPACITY LIMITED KINETICS The rate of elimination remains constant irrespective of drug concentration OR a constant amount of drug is eliminated in unit time ZERO ORDER (LINEAR) KINETICS: Rate of elimination is constant and is unrelated to the amount of drug in the body. 1hr 10mg 2hr 20mg 3hr 30mg 10hr 100mg e.g.-ethyl alcohol Zero order kinetics – t ½ with dose since CL progressively as dose is increased. Half life of the drug is never constant FIRST ORDER TO ZERO ORDER Phenytoin Tolbutamide Theophylline Warfarin Aspirin Phenytoin, Aspirin ↓ At low doses, follow first order kinetics As the plasma conc. increases Elimination processes get saturated ↓ Kinetics changes over to zero order (saturation kinetics) PLASMA HALF LIFE It is the time required for the plasma concentration of the drug to decrease by 50% of its original value . • Initial rapidly declining (α) phase – due to distribution • Later less declined (β) phase – due to elimination • At least two half-lives (distribution t1/2 and elimination t1/2) can be calculated from the two slopes. The elimination half-life derived from the β slope is simply called the half life of the drug . Mathematically ,elimination t1/2 is = ln2/k * ln2 is the natural logarithm of 2 (or 0.693) * k is the elimination rate constant of the drug. i.e. the fraction of the total amount of the drug in the body which is removed per unit time . Eg: 2g of drug present in the body & 0.1g is eliminated every hour then k =0.1/2=0.05 or 5% per hour . k=CL/v , therefore t1/2 =0.693xV/CL 1 t1/2 = 2 t1/2 = 3 t1/2 = 4 t1/2 = Nearly complete elimination occurs in 4 -5 half life Half life of Aspirin is 4hrs, Digoxin =40 hrs, First order kinetics – t1/2 remains constant because V and CL do not change with dose Zero order kinetics – t1/2 increases with dose because CL progressively decreases as dose is increased (elimination process get saturated) 50% drug is eliminated ; 75% ; (50% + 25%) 87.5% ; ( 75% +12.5%) 93.75% (87.5% + 6.25%) Digitoxin is 7 days. Half life is useful in estimating : time to reach steady state concentration duration of drug action time for plasma concentration to fall after the drug has stopped determine the frequency of drug administration LOADING DOSE Single or few quickly repeated doses given in the beginning to attain target concentration rapidly loading dose= Target Plasma conc X Vd bioavailability Single dose – Loading dose 7 Plasma Concentration 6 Therapeutic level 5 4 3 Repeated doses – Maintenance dose 2 1 0 0 5 10 15 Time 20 25 30 MAINTENANCE DOSE Drugs are administered in such a way so as to maintain a steady state of drug in the body THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING Monitoring drug therapy by measuring plasma concentration of a drug for the benefit to patient by achieving maximum therapeutic benefit with minimum side effects. INDICATIONS With narrow therapeutic index/low safety margin Eg: Digoxin , Phenytoin, carbamazepine ,Gentamicin Antidepressants , Lithium. Altered physiological states affecting drug concentration Check patient compliance Poisonings Failure of drug response without any reason Drug response Used for adjustment of doses To check bioavailability FIXED DOSE COMBINATION It is the combination of two or more drugs in a single pharmaceutical combination Advantages: Increases patient compliance Synergistic combination. Eg: Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim: Cotrimoxazole Levodopa + Carbidopa: Parkinsonism Estrogen + Progesterone : Oral contraceptive Reduced side effects - the side effect of one component may be counteracted by the another Eg: thiazide +potassium sparing diuretic Reduced cost Prevents emergence of antimicrobial resistance Increased efficacy (produce Max effect of the drug) Disadvantages: The patient may not actually need all the drugs present in a combination: he is subjected to additional side effects and expense . Inflexible fixed dose ratio Incompatible pharmacokinetics Difficult to identify one particular drug causing harmful effect Increased toxicity due to inappropriate combinations Physician and pharmacists ignorance of the contents. FIXED DOSE COMBINATION: FDC (FIXED DOSE RATIO COMBINATIONS) Levodopa + Carbidopa: Parkinsonism Isoniazid + Rifampicin + Pyrazinamide: Tuberculosis. Ferrous sulfate + Folic acid: Anemia of pregnancy. Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim: Cotrimoxazole. Amoxicillin + Clavulanic acid: Augmentin. Estrogen + Progesterone : Oral contraceptive Aspirin + Codeine: As an analgesic. PROLONGATION OF DRUG ACTION To decrease frequency of drug administration and improve compliance Avoiding large fluctuations in plasma concentration Maintaining the drug effect overnight without disturbance METHODS A. For orally administered drug: Enteric coated e.g., erythromycin Sustained release preparation e.g: Diclofenac B. For parenterally administered drug: 1) By decreasing the vascularity of the absorbing surface : This is achieved by adding a vasoconstrictor to the drug . Eg: Adrenaline with local anesthetics Adrenaline prolongs the duration of action and reduce the systemic toxicity of local anesthetics. And also minimizes bleeding in the operative field . Adding Adrenaline is contraindicated in cardiovascular disease patients . 2) By decreasing the solubility : Decreasing the solubility of the drug by combining it with a water insoluble compound . Eg: Injection penicillin G has a duration of action of 4-6 hours Injection penicillin G +Procaine : procaine penicillin G has a duration of action of 12-24 hours and also less painful. 3) Injecting the drug in oily solution : Depot progestins (depot medroxy progesterone acetate ) 4) Pellet implantation : Norplant for contraception 5)Pilocarpine ocusert and progestasert 6)Transdermal patch 7) By increasing the plasma protein binding of the drug : Eg: Sulphadiazine is less bound to plasma proteins and has duration of action of 6 hours . Sulphadoxine is highly protein bound and has a duration of action of one week 8) By inhibiting the drug metabolism : Anticholinesterases (Physostigmine ,neostigmine )prolongs the duration of action of Ach by inhibiting the cholinesterases 9) By delaying renal excretion of the drug : Probenecid prolongs duration of action of pencillin/Cephalosporins THANK YOU