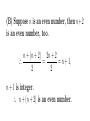* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (A) A number is an integer. Two numbers can be divided. Dividing a
Survey
Document related concepts
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Series (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
(A) A number is an integer. Two numbers can be divided. Dividing a number x by another number y determines how many y’s are in x. If y is 2, and x can be divided by y with no remainder, then x is even. If x is even and another number z is even then their sum is also even. (B) Suppose n is an even number, then n+2 is an even number, too. 2n + 2 n + (n + 2) ... = = n + 1, 2 2 n + 1 is integer. ... n + (n + 2) is an even number. (C) An even number is every second number from 0. (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, . . .) No matter how big an even number is, its final digit place will always be an even number. The diference between 2 consecutive even numbers will be consistently 2. If you add 2 numbers, assuming they are even, then the sum will also be even. (D) a = an even number b = an even number An even number is a number such that when they are divided by 2 the remainder is 0. Since its remainder is zero, no matter how many 0s you add to 0 the result is still 0, for example 0 + 0 + 0 is still zero. If 2 numbers that are even add to each other, its remainder is still 0. Therefore the sum of 2 even numbers is an even number. 0 |2| is the smallest even number. (E) 1 An even number can always be divided by 2 without getting fractions. 2 Every even number is a multiplication of the num ber 2 (by 1). 3 Adding two even numbers means adding two num bers that are multiplication of 2 (by 1,2). 4 The sum of two even numbers is the multiplication of 2 (by 2,3). 5 The sum of two even numbers is an even number (by 4,0). (F) Every even number is always 2 more than the previous even number. When you add 2 even numbers together, you answer will always be divisible by 2, because the number is simply a specific number of 2s all added together. Here’s an example: 16 an be broken down to 2+2+2+2+2+2+2+2. When you’re only adding 2s together you know your number will be divisible by two, which proves the number is even, because every number is divisible by 2. (G) 1) An even number is one which, when divided by 2, results in a whole number. (Examples: 42 = 2, even; 25 = 2.5, not even) 2) Even numbers must be whole numbers. 3) A number divisible by 2, resulting in a whole number, is even. 4) An odd number is a number that when divided by 2 results in a non-whole number. (Example: 25 = 2.5) 5) Even numbers always increment by 2, starting at 2. (Example: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, ...) 6) Addition is the process of counting and totaling the values of x and y numbers. (Example: 2 + 3 = 5) 7) The addition of 2 whole numbers equal a whole number; like = like. (Example: 2 + 2 = 4) 8) Even numbers are always whole numbers. Adding two even numbers is a whole number. 9) If two items independently are divisible by 2, their sum will also be divisible by 2. (Example: 42 = 2, 62 = 3, 6 + 4 = 10, 10 2 = 5) 10) The sum of two even numbers equal a whole number divisible by 2 that results in a whole number. (Example: 6 + 4 = 10, 10 2 = 5) 11) Two even numbers added together result in an even number. (H1) Formula: a + b = c, where c, a, and b are even numbers. By definition, an even number is a number that can be divided by two and stay a whole number. If we use the formula, we can get the following table going from the lowest even numbers to the highest: Based on the results in this table, we can cona b c clude that variable c will always be equivalent 2 2 4 to an even number. Also seen in table below, 2 4 6 the c variable from this table was utilized in the 2 6 8 second formula c/2 = d. This table proves that 2 8 10 variable c fits the definition of an even number 2 10 12 by always being a whole number when c is di2 12 14 vided by two, in which c is the sum of two even 2 14 16 numbers. 2 16 18 (H2) c 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 d 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 To cover the only number assigned to a that c did not cover, another table was created by using the formula a/2 = d, proving that all values of a and b are even values by definition. [This other table can be summarized by saying: When a = 2, d = 1.]