* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Sound level meter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Peak programme meter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
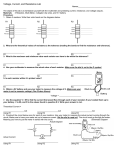
Digital Multimeter Introduction • Choosing the right meter Category • Category ratings are designed to protect users from transient overvoltage conditions (intermittent voltage spikes caused by electrical equipment surges during starting, capacitors, inductive circuits, and lightning strikes) • It is these unintended and intermittent transient voltage spikes that can be dangerous to users with too low of meter category rating Digital Multimeter Introduction • Choosing the right meter Category 1. With the likely hood of working in multiple different category environments always choose a meter that will be safe for working on the HIGHEST category that could potentially be accessed 2. Choose a Steady State Voltage rating that meets the maximum voltage you will encounter 3. ALWAYS choose the Category FIRST and then a steady state voltage value − A CAT III–600V meter will provide far superior transient voltage protection than CAT II–1000V meter Digital Multimeter Introduction • Choosing the right meter Category 4. TEST LEADS: Be sure your test leads have an equal, or HIGHER, Category and Voltage rating than the chosen meter – Meter system only as-good-as its components (as strong as the weakest link) – Quality Leads should be rated CATIII 1,000V and CAT IV 600 and UL Listed – Double insulated Digital Multimeter Introduction 4. TEST LEADS: – Protective tips and accessory clips make connecting to circuits and components easier and safer, but change the category rating of the test leads. • With Protective tips: 1000V CAT III & 600V CAT IV • WithOUT Protective tips: 1000V CAT II & 600V CAT III (LOWER Rating) Review for Understanding 1. What are the two types of signals commonly converted and displayed on a DMM? 2. True of False: DMMs can measure a wide range of signals with accuracy. 3. How many ohms is 92.2 kΩ 4. Explain the 4 basic operations DMMs help us to perform. 5. Define High Impedance. Why is it important when testing electronic circuits?