* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics - Mr. Brown`s Science Town
Survey
Document related concepts
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
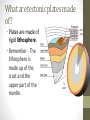
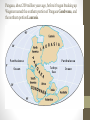
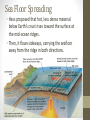
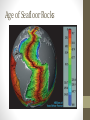
Plate Tectonics The Dynamic Interior of the Earth Review of Earth’s Interior: 1. Name, in order going from the center of the Earth to where we live, the four major layers of the Earth. 2. What composes the lithosphere? 3. How do the two layers closest to the center of the Earth differ in their composition? 4. Describe how scientists determine the composition of the different layers of the Earth. If you look at a map of the world, do you notice anything interesting about the shapes of the continents? Plate Tectonics • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= _5q8hzF9VVE • The Earth’s crust is divided into 12 major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. Plate Tectonics • The plate interactions cause the Earth structures (mountains, trenches, etc.). • Tectonic: deformation of the crust because of a plate interaction. What are tectonic plates made of? • Plates are made of rigid lithosphere. • Remember - The lithosphere is made up of the crust and the upper part of the mantle. Theory of Continental Drift • Proposed by Alfred Wegener in early 1900’s. • He hypothesized that the continents were once joined together in a single large land mass he called Pangaea Theory of Continental Drift • Pangaea split apart and the continents moved gradually to their present positions • Process is known as Continental Drift Pangaea, about 200 million years ago, before it began breaking up. Wegener named the southern portion of Pangaea Gondwana, and the northern portion Laurasia. The continents about 70 million years ago. Notice that the breakup of Pangaea formed the Atlantic Ocean. India’s eventual collision with Eurasia would form the Himalayan Mountains. Learning Check • What layer of the Earth composes the tectonic plates? • How many “major” plates make up the Earth? • Who developed the theory of plate tectonics? • Describe Pangaea. Evidence of Continental Drift 1. Continents fit together like a puzzle. • Ex. - The Atlantic coastlines of Africa and South America. More Evidence… 2. Fossils of several plants and animals of the same species found on different continents. Ex. Mesosaurus Some More Evidence 3. Rock and Mountain Correlation. Identical rocks and mountain structures have been found on either side of the ocean. • The order of rock layers in South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia show remarkable similarities. Last Piece of Evidence 4. Ancient climate information. • Coal has been found in cold regions and glacial evidence has been found in warm climates. Another Learning Check… 1. Explain at least 3 pieces of evidence used to support Wegener’s theory of continental drift. Was Wegener Correct? • Everyone agreed that Wegener’s evidence was compelling. But wouldn’t we feel the movement? • Also, wouldn’t there be evidence to show that the continents were still moving today? • Wegener was a meteorologist and his theory was not well accepted. (He died on an expedition in Greenland collecting ice samples) Holes in Wegener’s Theory… • One reason scientists had a hard time with Wegener’s theory is that there was no mechanism for the continents motion. Sea Floor Spreading • Henry Hess • 1960’s • Using new technology, radar, he discovered that the seafloor has both trenches and mid-ocean ridges. • Proposed the seafloor spreading theory. Sea Floor Spreading • Hess proposed that hot, less dense material below Earth’s crust rises toward the surface at the mid-ocean ridges. • Then, it flows sideways, carrying the seafloor away from the ridge in both directions. Sea Floor Spreading • As the seafloor spreads apart at a midocean ridge, new seafloor is created. • The older seafloor moves away from the ridge in opposite directions. • This helped explain how the crust could move—something that the continental drift hypothesis could not do. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hmM lspNoZMs Evidence of Seafloor Spreading • In 1968, scientists aboard the research ship Glomar Challenger began gathering information about the rocks on the seafloor. • Scientists found that the youngest rocks are located at the mid-ocean ridges. Age of Seafloor Rocks