* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virtual Lab
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Computational phylogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Sequence alignment wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
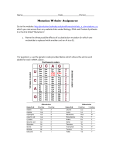
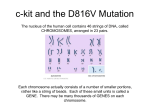
Name:_________________________________________ Date:________________ Per:_______ DNA Mutations Virtual Lab: 55 Points DUE: ___________________________________________ Background: Mutations involve a physical change to genetic material that results in the abnormal encoding of protein sequences. The impact of these changes can be insignificant or devastating. In this lab, you will complete mRNA and protein sequences based on the information provided. You will be given a starting mRNA sequence, its associated amino acids, and a mutation rule. Use these to construct the mutated mRNA sequence. Compare the original and mutated sequences to see the impact of the mutation. There are several types of mutations: 1. FRAMESHIFT, meaning the reading “frame” changes, changing the amino acid sequence. There are two types: DELETION (a base is lost) INSERTION (an extra base is inserted) 2. POINT, a single base is changed, which can cause a change in the amino acid. This is known as: SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE mutation If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT mutation. If a substitution changes the amino acid to a “stop,” it’s called a NONSENSE mutation. Procedure: Step 1 – Google “glencoe dna mutations virtual lab” and click the first link. Step 2 – Click the Mutate Button to see a sequence and a mutation rule. BE SURE YOU ARE GIVEN THE ORIGINAL SEQUENCE. If not, click “mutate” until you have an original sequence. Step 3 – Read and apply the mutation rule to the original sequence to determine the mutated sequence. Construct the mutated sequence by dragging nucleotides and amino acids to their new locations. Use the information on your codon chart to identify the amino acids associated with the mutated mRNA sequence. Click a nucleotide or amino acid to remove it. Step 4 – Click “check” to check your answer to be sure it is correct. Fill in Data Table 1. Step 5 – Click the Mutate Button again to generate another sequence and complete steps 1-3 again. Fill in Data Table 2. Answer the analysis questions. Name:_________________________________________ Date:________________ Per:_______ Data Table 1: 16 pts Original mRNA Sequence Original Amino Acid Sequence Mutated mRNA Sequence Mutated Amino Acid Sequence Data Table 2: 16pts Original mRNA Sequence Original Amino Acid Sequence Mutated mRNA Sequence Mutated Amino Acid Sequence Name:_________________________________________ Date:________________ Per:_______ Analysis Questions: 1. Which type of mutation (substitution, insertion, or deletion) occurred in Data Table 1 and how do you know? 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Describe the differences between the original and mutated sequences. 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. How many amino acids were changed? 1pt_____________________________________ 4. What do you think will be the impact of this mutation? Why? 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which type of mutation (substitution, insertion, or deletion) occurred in Data Table 2 and how do you know? 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 6. Describe the differences between the original and mutated sequences. 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 7. How many amino acids were changed? 1pt_____________________________________ Name:_________________________________________ Date:________________ Per:_______ 8. What do you think will be the impact of this mutation? Why? 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 9. Explain why all mutations are not necessarily harmful. 3pts ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________