* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations Worksheet
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
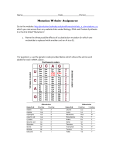
Point Mutations Practice Name Per. ___________ There are several types of genetic point mutations (a change in only one letter of the genetic code): FRAMESHIFT, meaning the reading “frame” changes, changing the amino acid sequence. DELETION (a base is lost) INSERTION (an extra base is inserted) SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE point mutation. If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT point mutation. If a substitution changes the amino acid to a “stop”, it’s called a NONSENSE point mutation. Complete the boxes below. Classify each as either Frameshift or Substitution mutations, then specify further with Deletion, Insertion, or type of substitution. Use the chart on p. 303 in your textbook or back of Protein synthesis notes to determine the amino acid sequence. Remember, RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine. Original DNA Sequence: T A C A C C T T G G C G A C G A C T mRNA Sequence: ___________________________________________________________________ Amino Acid Sequence (use 3-letter abbreviation): Mutated DNA Sequence #1: (Circle the change) T A C A T C T T G G C G A C G A C T What’s the new mRNA sequence? What will be the changed amino acid sequence? What kind of mutation is this? ________________________________ sub-type? ____________________________________ Describe effects ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Mutated DNA Sequence #2 (from original DNA): T A C G A C C T T G G C G A C G A C T What’s the new mRNA sequence? What will be the changed amino acid sequence? What kind of mutation is this? ________________________________ sub-type? ____________________________________ Describe effects ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Mutated DNA Sequence #3: (from original DNA): T A C A C C T T C G C G A C G A C T What’s the new mRNA sequence? What will be the changed amino acid sequence? What kind of mutation is this? ________________________________ sub-type? ____________________________________ Describe effects ___________________________________________ Mutated DNA Sequence #4: (from original DNA): T A C A C C T T G G C G A C A A C T What’s the new mRNA sequence? What will be the changed amino acid sequence? What kind of mutation is this? ________________________________ sub-type? ____________________________________ Describe effects ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Mutated DNA Sequence #5: (from original DNA): T A C A C C T T G G G A C G A C T What will be the new mRNA sequence? What will be changed the amino acid sequence? What kind of mutation is this? ________________________________ sub-type? ____________________________________ Describe effects ______________________________________________________________________________________________ Analysis Questions: 1. Which type(s) of mutation results in the most devastating change to the protein? Explain for each 2. Which type(s) of mutation(s) is/are responsible for new variations of a trait? Explain for each. 3. Which types of mutations stop the translation of the mRNA? Explain for each. 4. Mutations in which cells get passed down to offspring?