* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download physical activity
Survey
Document related concepts
Food and drink prohibitions wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Food studies wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Obesity in the Middle East and North Africa wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
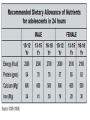
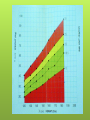
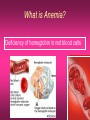
Nutrition & Physical Activity Nutrition: Why should you care ? Happiness is nothing more than good health and a bad memory. Albert Schweitzer Physical Growth Body image Brain Daily activities Sports performance Prevention of diseases Healthy Diet: Why is it important in this age ? Deposition of muscles You gain 25% of adult height, 50% of To become a healthy adult in future adult weight and 40% of adult bone mass during adolescence. Healthy Diet: How does it prevent diseases ? Obesity/under-nutrition Hypertension/heart disease Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Osteoporosis/Dental caries Anemia Vitamins and Mineral deficiencies Cancer Healthy Diet: Deciding the right amount Actual need varies with physical activity Physically active people have higher energy needs If you have low physical activity then you can become obese even with low intake. Therefore, Energy intake should balance energy expenditure. Healthy Diet: Food intake Carbohydrates 6-11 servings e.g. Rice, Chapati Protein-based e.g. Milk, Milk products 2-3 Salads, Vegetables (3-5) Fruits (2-4) Meat, egg/dal 2-3 Increase fiber Decrease oily foods ‘No’ to soft drinks Recommendations of IAP: Indian Pediatrics 2004; 41:559 Courtesy – Dr.Swati Bhave, 2005. FATS CARBOHYDRATES Major and immediate source of energy. Complex carbohydrates recommended High-sugar foods not preferred. Grains, cereals, fresh fruits, vegetables Source of essential fatty acids. Unsaturated fat recommended. e.g. Corn, cottonseed, Til oil, soybean, and sunflower oils contain about 50% polyunsaturated fat. Saturated fats increase cholesterol levels. PROTEINS Daily requirements Boys = 0.29-0.32 g/cm height Girls = 0.27-0.29 g/cm height 0.8 – 1.2 g/kg bodyweight High intensity athletes = 1.21.8 g/kg Pulses, lentils, soya, dairy products and animal food products. Looks can be deceiving Iron Zinc Iodine Calcium Increased need during adolescence Needs met by a well-balanced diet Vitamin D Thiamin Riboflavin Niacin Vitamin B 12 Vitamin C Folic acid Sources – Fruits, fresh milk, sprouted beans etc. Iron Anemia is most common nutritional deficiency in adolescents. Increased red cell mass during adolescence. Daily need Boys = 12 mg/d & Girls = 18 mg/d Green leafy vegetables, jaggery, wet dates, whole-grain, dried beans, peas & dried fruits, nuts & fortified wheat products, eggs, red meat etc. Zinc Second most abundant trace mineral in the body. (next to iron) Necessary for normal growth. Clinically apparent deficiency rare. Daily need = 15 mg Green leafy vegetables, wheat germ, whole grains meat, cheese, eggs, poultry, liver. Calcium Most bone adolescence. mass acquired during Typical intake of calcium = about 800 mg/ d Daily need = 1300 mg Consumption of soft drinks & caffeine contribute substantially to low calcium intake in adolescents. Bone mass deficiency may is irreversible. Milk and its products, yogurts, cheese, paneer, banana. What is ‘Normal’ eating ? Eating is regulated by hunger and satiety i.e. feeling full Eating should be at regular intervals Choose healthy snacks and food If you eat healthy and exercise regularly you can occasionally enjoy high fat and high calorie junk foods. Good eating habits Maintain hygienic habits Eat slowly, chew properly Avoid TV viewing or reading while you eat Small frequent meals Never skip meals, specially breakfast Don’t overeat Do healthy snacks exist ? Yes, and in plenty. Snacks like fresh fruits, sprouted beans and nuts are nutritious and healthy Avoid energy dense snacks like burgers “Empty calories” – High sugar drinks Aerated drinks interfere with bone density and can damage teeth Why is Fast Food unhealthy ? High in calorie, fat, sodium and low in fiber which can cause Obesity, Hypertension, Heart diseases, Diabetes, Cancer etc. Contains preservatives Choose low-calorie and low-fat meals, snacks and desserts Have low fat or skim milk drinks. The Middle Path: Making Junk food healthy Replace the Cheese with Paneer or low-fat cheese Add plenty of vegetables Replace frying with grilling or baking Replace white bread, maida noodles or maida pizza base with whole-grain wheat Have low-fat or skimmed milk based products Breakfast: Brain Food Improves performance in studies Improves physical activities Does not contribute to overweight Keeps you healthy The most important meal Skipping breakfast associated with obesity High sugar breakfast causes a high sugar level which dips fast making you more hungry and you eat more sugary food PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: Why is it important ? PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: Types of physical activity Daily Chores: walking, climbing stairs, cycling, household activities, etc. Exercise: planned & structured subset of leisure time physical activity undertaken for improving or maintaining physical fitness. 30-60 minutes every day Sports: involves competition. It may become an occupation. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: Importance This includes : Cardio-respiratory i.e. Heart & Lung fitness Muscle strength Endurance & flexibility Television and Obesity Excessive TV watching is associated with weight gain specially when associated with increased snacking with junk food and aerated drinks TVsterol Combine TV watching with physical activity like stationary bicycling, or spot jogging PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: Keeping in shape It is recommended to have 30-60 min. moderate physical activity on weekdays, four days a week It is not necessary to exercise continuously Can be divided into 10 -15 minutes of activities several times through the day Nutrition & Exercise: Myths × Girls don’t need muscle stretching exercises × You can become obese if you leave exercise × Expensive food and vitamins are needed for good health and machines for exercise × Sona-chandi × Health drinks Key points Proper Nutrition & Regular Physical Activity are very important for • Growth • Prevention of illness • Future health What is Anemia? Deficiency of hemoglobin in red blood cells 26 • Oh!... I am so tired… • Out door games? Not for me! • Why can’t I remember better? • I fall sick so often… • I just can’t cope… • My mother died… when I was born. 27 Consequences of anemia School children • • • • • Impaired cognitive performance Diminished IQ Attention deficit disorder Decrease in school performance Decrease in learning ability 28 Consequences of anemia All Age Groups • • • • • • Increased tiredness Disinterest in surroundings Increased risk of death & disability Increased risk of having premature babies Poor exercise tolerance - tiredness Impaired immune response – susceptible to infections 29 Anemia is preventable • Nutritional anemia • Anemia is most common nutritional deficiency in Adolescents beause of Increased red cell mass. • Daily need: Boys = 12 mg/d & Girls = 18 mg/d • Green leafy vegetables, jaggery, wet dates, whole-grain, dried beans, peas & dried fruits, nuts & fortified wheat products, eggs, red meat etc. • Anemia due to worms in the intestines • Acute blood loss anemia – accidents, child birth • Chronic blood loss anemia – heavy periods, piles 30