* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War - cloudfront.net
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
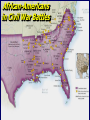
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
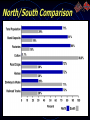
The Civil War Girding for War 1861 - 1865 The War Begins • March 4, 1861: Lincoln takes office • Vows to “preserve, protect, & defend the Union” • April 6: Lincoln warns So. Carolina he is going to send supplies to Fort Sumter at Charleston • April 12: South Carolina fires on Ft. Sumter •After 33 hours of bombardment Ft. Sumter falls •War has begun Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 • April 15: Lincoln calls for 75,000 volunteers & a naval blockade on the South • Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, & Tennessee secede - Confederacy is now 11 states The Border States • Lincoln recognized the importance of the border states •Maryland, Missouri, the mountain areas of western Virginia, & most importantly Kentucky Non-Emancipation • To keep the Border States in the Union, Lincoln announced that he was not fighting to free the blacks •Also somewhat pacified the Butternut areas of the Ohio River “My paramount object is to save the Union, and is not either to save or destroy slavery…If I could save the Union with out freeing any slave I would do it, and if I could save it by freeing all the slaves I would do it, and I could save it by freeing some and leaving others alone, I would also do that.” - Abraham Lincoln Native Americans • Cherokee Nation, themselves slave owners, sided with the Confederacy & “seceded” from the Union • Northern Plains Indians sided with the Union Northern Advantages • North’s population was 22 million vs. South’s 9 million - 1/3 of whom were slaves • Union had 3 times as many service age men Men Present for Duty during Civil War • North eventually recruited roughly 200,000 AfricanAmericans as soldiers - the South did not use slaves • North had the stronger & more varied economy most of the manufacturing, 2/3 of railroads • North had more agriculture & minerals • North already had an organized government & a wealthy treasury • North was fighting for the preservation of the Union Southern Advantages • South fighting a defensive war - a draw would be a victory • North had to invade, conquer, & control an area the size of western Europe • Most Southern men were from farms & knew how to ride & shoot • South had a strong military history •More U.S. Army officers were from the South including General Robert E. Lee • South had hope for support from England & other European countries North/South Comparison North vs. South: Resources The Diplomatic Front • Britain •British ruling class had strong ties to the aristocratic South •British laboring class backed the industrial free labor North •Britain’s navy could have broken the blockade •Britain worried about the Union attacking Canada • In 1861, the British had an oversupply of cotton • North shipped much needed grain to England • France •Napoleon III placed Maximillian on the throne of Mexico until 1867 The Trent Affair • Union navy apprehended two Confederate diplomats from a British ship •Northerners rejoiced at getting even for impressment of 1812 • British prepared for war against Union • Loss of Atlantic cable led to delays & the crisis cooled down • Lincoln freed the two diplomats • Seward congratulated the English on accepting the illegality of impressment & seizure The Alabama • British shipyards built the commerce raider ship The Alabama - not a warship as it was unarmed • Ship went to the Azores with British crew & took on weapons • Alabama caused havoc to American shipping • Finally sunk off the coast of France in 1864 • Charles Francis Adams •Son of JQ Adams •Chief Union diplomat to Great Britain •Presented persistent claims for the destruction of US shipping to Britain • Britain ultimately gave in & confiscated other ships being built in England • Commerce raiders put a serious, but not crippling, dent in the American merchant Marine The Laird Rams • 1863: British navy yard began building two Confederate warships with iron rams • British fearing war & US invasion of Canada bought the ships for the British navy • 1872 Britain submitted to US claims & paid the Americans $15 million in damages • 1866 & 1870 Irish Fenians launched invasions into to Canada for Irish independence Wartime Liberties? • Saving the Union required circumventing some areas of the Constitution •Naval blockade of South •Increased size of army •Extended enlistment time •$2 million to citizens for military purposes •Suspended habeas corpus to arrest anti-Unionists •Ex Parte Merriman, 1861 •864 people held w/o trial •“Supervised” voting in Border States •Outlawed slavery in all national territories • Jefferson Davis unable to do the same in the South •No strong central gov’t in the South •Davis rigid & unpopular •South willing to lose the war before losing states’ rights Draftees • Initially, Union army comprised of volunteers • 1863: Congress passes 1st conscription law •Wealthier could hire substitutes or pay a $300 exemption • New York City Draft Riots broke out - Irish laborers attacked blacks • Union army was 90% volunteer - many went AWOL & reenlisted to get bounty money • Roughly 200,000 AfricanAmerican soldiers fought for the Union beginning in 1862 African-American Recruiting Poster The Famous 54th Massachusetts August Saint-Gaudens Memorial to Col. Robert Gould Shaw African-Americans in Civil War Battles Black Troops Freeing Slaves • South relied mainly on volunteers •1862: began conscription of men 17-50 yrs. Old •Did not enlist slaves until 1865 • Both sides had over 200,000 deserters Economic Problems • Union financing: •1st Ever Income Tax •Paid 2/3 cost of war •Excise taxes •Tobacco & alcohol •Morrill Tariff Act (1861) •10% tariff increase •Bond sales •Borrowed more than $2.6 billion in bonds - sold by Jay Cooke & Company •1863: National Banking System •created a standard currency & replaced the BUS of 1836 • Union also issued currency called Greenbacks •Over $450 million dollars not solidly backed by gold •Currency flood led to inflation hurting workers •Fluctuated in value (39 cents) • Confederacy’s finances wrecked by… •Inflation •Blockade •$400 million in worthless bonds •10% farm produce tax •Over $1 billion dollars in treasury notes (1.6 cents) Inflation in the South “Shoddy Millionaires” • Wartime expansion in North brought: •Inflation •Huge profits •New millionaire class •Speculation •Profiteering/Dishonesty •New technology • Marks beginnings of “Gilded Age” • 1859: oil discovered in Titusville, PA beginning the petroleum industry • Only industry hurt was shipping by southern commerce raiders • Westward expansion: •Homestead Act (1862) •Free land to pioneers •Morrill Land Grant Act (1862) •Ag. & mechanical colleges •Pacific Railway Act (1863) •Northern route for railroad