* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
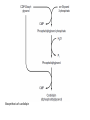
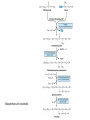
Metabolism of Acylglycerols & Sphingolipids BIOMEDICAL IMPORTANCE • Acylglycerols constitute the majority of lipids in the body. • Obesity, diabetes,and hyperlipoproteinemia • Cell membranes • Lung surfactant • Hormone second messengers • Platelet-activating factor • cell adhesion and cell recognition • as receptors for bacterial toxins • ABO blood group substances • Glycolipid storage diseases TRIACYLGLYCEROLS • HYDROLYSIS INITIATES CATABOLISM OF TRIACYLGLYCEROLS – – – – – Lipolysis (Lipase) adipose tissue free fatty acids Serum albumin Uptake into tissues • Oxidized or reesterified – Glycerol • Glycerol kinase Overview of acylglycerol biosynthesis • • • • Phosphatidate Is the Common Precursor Both glycerol & fatty acids must be activated Glycerol 3-phosphate Activation of fatty acids – acyl-CoA synthetase • Acyltransferase • Most of the activity of these enzymes resides in the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell, but some is found in mitochondria • Choline or ethanolamine must first be activated • Cardiolipin Biosynthesis of cardiolipin GLYCEROL ETHER PHOSPHOLIPIDS • BIOSYNTHESIS – in peroxisomes • Plasmalogens – 1-alkyl-2-acylglycerol 3-phosphoethanolamine • Plateletactivating factor (PAF) – 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-3- phosphocholine • Involved in – Inflammation, chemotaxis, and protein phosphorylation. Biosynthesis of ether lipids Biosynthesis of ether lipids • Phospholipases – allow degradation & remodeling of phosphoglycerols Metabolism of phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) Sites of the hydrolytic activity of phospholipases • Long-chain saturated fatty acids are found predominantly in the 1 position of phospholipids • the polyunsaturated acids (eg, the precursors of prostaglandins) are incorporated more into the 2 position • The incorporation of fatty acids into lecithin; by, – Complete synthesis of the phospholipid – Transacylation between cholesteryl ester and lysolecithin – Direct acylation of lysolecithin by acyl-CoA SPHINGOLIPIDS • Formed from CERAMIDE Biosynthesis of ceramide. Biosynthesis of sphingomyelin Glycosphingolipids • Simple – Cerebrosides • Galactosylceramide (GalCer) • Glucosylceramide (GlcCer) • Complex – Gangliosides • Contain a sialic acid, usually Nacetylneuraminic acid • activated sugars – Glycosyl transferases,Golgi apparatus • active sulfate Biosynthesis of galactosylceramide and its sulfo derivative. (PAPS,“active sulfate,” adenosine 3′-phosphate-5′-phosphosulfate.) Glycosphingolipids • Constituents of the outer leaflet of plasma membranes – Cell adhesion and cell recognition – Antigens – Receptors Biosynthesis of gangliosides CLINICAL ASPECTS • Respiratory Distress Syndrome – Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine • Multiple Sclerosis – a demyelinating disease • Loss of both phospholipids (particularly ethanolamine plasmalogen) and of sphingolipids from white matter • Lipidoses – Sphingolipidoses (lipid storage diseases) – a Lysosomal disorder CLINICAL ASPECTS • Features – Complex lipids containing ceramide accumulate in cells, particularly neurons • The rate of synthesis of the stored lipid is normal • The enzymatic defect is in the lysosomal degradation pathway Examples of sphingolipidoses SUMMARY • Triacylglycerols – The major energy-storing lipids • Phosphoglycerols, sphingomyelin, and glycosphingolipids – Amphipathic • Have structural functions in cell membranes – Specialized roles • Triacylglycerols and some phosphoglycerols are synthesized by progressive acylation of glycerol 3-phosphate. • ether phospholipids – Plasmalogens and platelet-activating factor (PAF) – Formed from dihydroxyacetone phosphate • Sphingolipids – formed from ceramide (N-acylsphingosine) • Gangliosides – Complex glycosphingolipids • Containing more sugar residues plus sialic acid • Disease processes – Phospholipids and sphingolipids • Respiratory distress syndrome (lack of lung surfactant) • Multiple sclerosis • Sphingolipidoses





































![The Digestive System A1 Notes! [PDF Document]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004372699_1-b2b83261c9e60c1b651a3d3ea2943ac8-150x150.png)