* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12v battery charger - Kaushik Science Projects
Survey
Document related concepts
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
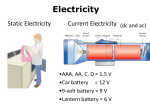
INTRODUCTION This is the circuit of a simple 12 volt battery charger for Lead Acid battery. It gives 12 volt and 5 Amps current for quick charging of the battery. If the battery is partially discharged, full charge will be attained in one hour. The circuit uses a 0-14 volt 5 Ampere Step down transformer and a 10 Amps Bridge rectifier module to convert AC to DC. Since pulsed DC is good for Lead Acid battery, a low value smoothing capacitor is used as C1.To monitor the charging status, Ampere meter is provided in the positive rail. LED act as the Charger on status. When the output is connected to the battery terminals, the meter shows a higher reading depending on the current flow into the battery. As the battery attains full charge, its terminal voltage rises to 13.8 volts and current through the meter ceases. The meter reading then returns to zero. This indicates the full charge state and the charging can be terminated. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM COMPONENTS REQUIRED 12V OUTPUT TRANSFORMER CONNECTING WIRE BATTERY (12V) WORKING: The circuit uses a 0-14 volt 5 Ampere Step down transformer and a 10 Amps Bridge rectifier module to convert AC to DC. Since pulsed DC is good for Lead Acid battery, a low value smoothing capacitor is used as C1.To monitor the charging status, Ampere meter is provided in the positive rail. LED act as the Charger on status. When the output is connected to the battery terminals, the meter shows a higher reading depending on the current flow into the battery. As the battery attains full charge, its terminal voltage rises to 13.8 volts and current through the meter ceases. The meter reading then returns to zero. This indicates the full charge state and the charging can be terminated. COMPONENT DESCRIPITON : TRANSFORMER: Transformer: Usually, DC voltages are required to operate various electronic equipment and these voltages are 5V, 9V or 12V. But these voltages cannot be obtained directly. Thus the a.c input available at the mains supply i.e., 230V is to be brought down to the required voltage level. This is done by a transformer. Thus, a step down transformer is employed to decrease the voltage to a required level. Some times transformers make the output voltage bigger than the input voltage, this is aSTEP UP TRANSFORMER. In a step up transformer there are more coils of wire on the secondary coil than on the primary coil. Some times transformers make the output voltage smaller than the input voltage, this is aSTEP DOWN TRANSFORMER. In a step down transformer there are more coils of wire on the primary coil than on the secondary coil. Transformers are used in the national grid. How a transformer works Alternating current (ac) in the primary coil (input coil) produces a changing magnetic field in the laminated soft iron core. The changing magnetic field induces a potential difference (voltage) in the secondary coil(output coil). BATTERY: WORKING Battery Construction Lead acid batteries used in the RV and Marine Industries usually consist of two 6-volt batteries in series, or a single 12-volt battery. These batteries are constructed of several single cells connected in series each cell produces approximately 2.1 volts. A six-volt battery has three single cells, which when fully charged produce an output voltage of 6.3 volts. A twelve-volt battery has six single cells in series producing a fully charged output voltage of 12.6 volts. A battery cell consists of two lead plates a positive plate covered with a paste of lead dioxide and a negative made of sponge lead, with an insulating material (separator) in between. The plates are enclosed in a plastic battery case and then submersed in an electrolyte consisting of water and sulfuric acid (see figure # 1). Each cell is capable of storing 2.1 volts. In order for lead acid cell to produce a voltage, it must first receive a (forming) charge voltage of at least 2.1-volts/cell from a charger. Lead acid batteries do not generate voltage on their own; they only store a charge from another source. This is the reason lead acid batteries are called storage batteries, because they only store a charge. The size of the battery plates and amount of electrolyte determines the amount of charge lead acid batteries can store. The size of this storage capacity is described as the amp hour (AH) rating of a battery. A typical 12-volt battery used in a RV or marine craft has a rating 125 AH, which means it can supply 10 amps of current for 12.5 hours or 20-amps of current for a period of 6.25 hours. Lead acid batteries can be connected in parallel to increase the total AH capacity. In figure # 2 below, six single 2.1-volt cells have been connected in series to make the typical 12-volt battery, which when fully charged will produce a total voltage of 12.6-volts.