* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
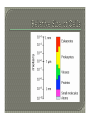
Download Domains Kingdom(s)
Survey
Document related concepts
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
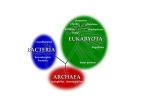
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
To be in biology first you must decide if something is living. Remember the Characteristics of Life: 1. Homeostasis 2. Organization 3. Metabolism 4. Growth 5. Adaptation 6. Response to stimuli 7. Reproduce 3 General Hierarchical • Arranged or grouped in order of rank. It is how biologists group and categorize organisms. It refers to the system in which groups are nested in each level. Higher levels are the most general and contain a collection of groups Lower levels are more specific. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Specific 4 General Living organisms that are closely related are grouped together. Domains are the broadest group. Species are the most specific group. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Specific 5 Domain Kingdom Eukarya Plantae Bacteria Animalia Phylum/ Division Chordata Proteobacteria Class Mammalia Gamma Proteobacteria Carnivora Enterobacteriales Order Asterales Family Asteraceae Genus Taraxacum Felis species officinale — Dandelion domesticus — House Cat Subspecies Felidae Canidae Enterobacteriaceae Panthera Canis Escherichia tigris — Tiger lupus coli familiaris — Dog lupus — Wolf 6 General Domain = Dear (biggest group) Kingdom = King Phylum (division) = Philip (David) Class = Came Order = Over Family = From Genus = Germany Species = Swimming (most specific) Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Specific 7 Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Carnivora Family: Felidae Genus: Felis Species: F. domesticus 8 There are three domains 1. Bacteria 2. Archaea Type of Cell Domains Kingdoms Prokaryote Bacteria Bacteria Prokaryote Archaea Bacteria Eukaryote Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia 3. Eukarya There are six kingdoms 9 Members of the Bacteria and Archaea are all prokaryotes (before a nucleus). They have no nucleus. Rather a single circle of DNA. They are unicellular, made of one cell. Prokaryote cells are small and simple. There are no organelles in prokaryote cells. Domains Kingdom(s) Bacteria Bacteria Archaea Archaea Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia 10 11 Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on earth. Both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without oxygen) respiration. Some use photosynthesis (make food using sunlight). E. coli 12 Archaea are less widespread than Bacteria. Differ from Eubacteria in • details of cell wall structure. • plasma membranes • DNA structure. Many Archaebacteria are methanogens. • This means that to produce energy Halobacteria sp. they use H2 gas to reduce CO2 to CH4 (methane), which releases energy. 13 Many Archaebacteria are adapted to extreme environments. • Thermophiles: “heat lovers.” Inhabit hot springs. Tolerate temps from 70 -- >110°C. • Halophiles: “salt lovers.” Require water that is 15-20% salt (seawater only 3% salt). Archaebacteria more closely related to the Eukarya than are the Eubacteria. 14 DNA is arranged in chromosomes in a nucleus. Include both 1. Unicellular (single-celled) organisms. 2. Multi-cellular (many-celled) organisms. Domains Kingdom(s) Bacteria Bacteria Archaea Archaea Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Cells larger and more complex than cells of Prokaryotes. Contain organelles. 15 Organelles are structures in cells specialized for particular tasks. • Mitochondria and chloroplasts. • Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living bacteria. • Over time they came to live inside the eukaryotic cells and established a symbiotic relationship. Domains Kingdom(s) Bacteria Bacteria Archaea Archaea Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia 16 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia 17 Kingdom Organisms Eubacteria Bacteria: Methanogens, Halophiles, Thermophiles, Psychrophiles Archaebacteria Bacteria, Cyanobacteria (bluegreen algae), Actinobacteria Protista Amoebae, green algae, brown algae, diatoms, euglena, slime molds Fungi Mushrooms, yeast, molds Plantae Mosses, angiosperms (flowering plants), gymnosperms, liverworts, ferns Animalia Mammals, amphibians, sponges, insects, worms 18 Two part name Binomial nomenclature Written in italics Genus is capitalized species is not capitalized When hand written underline each name individually Common Name Genus Specie s Sub-species Bengal Tiger Panthera tigris tigris Siberian Tiger Panthera tigris altaica Humans Homo sapiens sapien 19 Common Name Genus Species Sub-species Bengal Tiger Panthera tigris tigris Siberian Tiger Panthera tigris altaica Humans Homo sapiens sapien Domestic Dog Canis lupus familiaris Domestic Cat Felis catus Dandelion Taraxacum officinale Douglas Fir Pseudotsuga menziesii Oregon Grape Berberis aquifolium Western Meadowlark Sturnella neglecta menziesii 20