* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 5A
Survey
Document related concepts
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
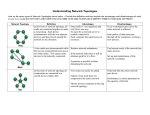
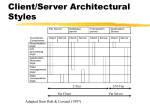
Section 7A Introduction to Computers Network A group of connected computers that communicate, exchange information and share resources home Benefits of Networks Users access programs and data simultaneously Users share printers and scanners Users communicate more easily Users backup their data more easily home File Server A computer that stores data files for networked users to access home Two Kinds of File Access Read-Only Read/Write home Levels of Access Rights or Policies Write access Supervisor access home Ways to Share Software on a Network Site license Network version home Shared Peripherals Multiple users send print jobs to a printer at the same time using spooling home Personal Communications E-mail Teleconferences Videoconferences home Backup The network manager makes regular backups home Two Types of Networks Local area network (LAN) Wide area network (WAN) home Packet Data is broken into small pieces--called packets--before being transmitted between networked computers home Packet Parts Header: has identifying information like type of data; data source and destination; and sequence number Payload: has the transmitted data home Protocol Rules and formats for sending and receiving data along the LAN home Kinds of Protocols TCP/IP IPX/SPX NetBEUI home Ways to Connect Similar LANs Hub Bridge Router home Gateway Connects Different LANs A gateway reads a packet header from one type of network and then adds a second header understandable by the second network home Other Networks Campus Area Networks (CANs) Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) Wide Area Networks (WANs) home Node A node is an individual computer on a network home Client/Server Networks Individual computers share the processing and storage workload with a central server home Peer-to-Peer Networks Sometimes called a workgroup Nodes share files and data with each other vs. client/server networks, where nodes share files and data only with the server home Network Features Topology: Physical or logical layout of cables and devices that connect the network nodes Media: wires and cables that carry data from source to destination Bandwidth: amount of data media can carry home Kinds of Topologies Bus topology Star topology Ring topology Mesh topology Wireless topology home Kinds of Media Twisted-pair cable Coaxial cable Fiber-optic cable Wireless networks home Network Technology Network technology is the kind of cabling equipment used to create a LAN home Examples of Network Technology Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Token Ring home Network Software The group of programs that manages the network resources is called the network operating system (NOS) home Examples of NOSs Novell NetWare Microsoft Windows NT Server Microsoft Windows 2000 Microsoft XP Microsoft .NET Server Linux home Section 7A Networking Basics Review Questions What is a network? What is a file server? What is a node? What’s the difference between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network? home