* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein Synthesis
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
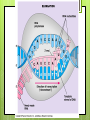
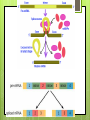
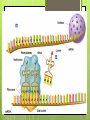
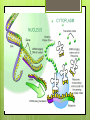
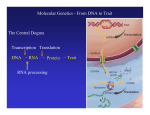
Protein Synthesis RNA Ribonucleic acid(RNA) consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the 2 strands found in DNA RNA nucleotides contain ribose isntead of deoxyribose. Ribose has an OH on the 2nd carbon RNA uses the nitrogenous base uracil instead of thymine. Uracil attaches to adenine Protein Synthesis Step 1 – Transcription is the transfer of the information from DNA to RNA Step 2- Translation is the process of reading the information on DNA and converting it into the amino acid sequences of the protein The specific sequence of genes (bases) on DNA directly determine the sequence of RNA, and therefore the types of proteins made Transcription Transcription is the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA Occurs in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes and the nucleus in eukaryotes Three key steps: Initiation, Elongation, Termination Transcription Initiation Promoter- a specific sequence of DNA that signals the start of transcription, like the starting line in a race RNA polymerase finds to the promoter on DNA RNA polymerase then separates the 2 DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds Transcription Elongation As RNA polymerase moves along DNA, it untwists the double helix and separates the strands RNA polymerase then adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of mRNA Follows the base-pair ruling, but now pairing U with A Transcription Termination Termination signal- sequence of bases in DNA that tell RNA polymerase to stop transcription Most common terminal signal is AATAAAA RNA polymerase is released from DNA and DNA will re-anneal RNA Modifications In eukaryotes, mRNA is modified before it’s sent out of the nucleus 2 major types of modifications Alterations of mRNA ends and RNA splicing RNA Modifications 5’ end received a guanine cap 3’ end received a poly-A tail, 50-250 adenine nucleotides These help protect mRNA from breaking down RNA Modifications Genes have stretches of nucleotides that don’t code for anything, called “junk DNA” (pre-mature mRNA) These regions are called introns or intervening sequences Coding regions = exons An enzyme called a spliceosome removes the introns and join the exons together (mature mRNA) Translation The building of a polypeptide (protein) from mRNA Uses transfer RNA (tRNA) to help Occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome Translation tRNA 3 – cloverleaf shape Contains anticodon – triplet of bases complementary to the bases (codon) on mRNA Carries corresponding amino acid on the other end that can detach bases needed per 1 amino acid Codons are 3 nucleotide sequences for an amino acid, found on mRNA The codons bind to the anticodons on tRNA, which will then bring the corresponding amino acid to form a protein Translation Ribosomes Made up of 2 subunits, large and small made of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Have special binding sites P site holds tRNA with amino acid chain A site hold the next tRNA Translation 3 stages: Initiation, Elongation, Termination Initiation mRNA and tRNA join Anticodon + complementary codon mRNA start codon is AUG tRNA is UAC and brings the “start” amino acid methianine Large and small subunits join, forming a functional ribosome around the RNA Translation Elongation Amino acids are added one by one by the following process mRNA codon binds with anticodon on tRNA Peptide bond is formed between the new amino acid and the last one tRNA moves over from A site to P site Translation Termination Elongation continues until a stop codon is reached (UAA, UAG, UGA) Polypeptide (protein) is released from ribosome and ribosome falls apart into the 2 subunits Gene Regulation Mutations- change in the DNA (gene) and only passed onto offspring if in the sex cells Gene Regulation Gene rearrangements- mutation that moves an entire set (of bases) to a new spot Transposition- gene moves Chromosomal- chromosome rearranges Gene Regulation Gene gene alteration- mutations that change a Point mutation- a single base is changed Base pair substitution- changes one base for another Silent- base pair substitution that gives the same amino acid, allowing for the protein to form Insertion- bases are added Deletion- bases are deleted Frameshift- an insertion or deletion that alters the codon reading, always occurs with insertion/deletions Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Prokaryotes only have ~2,000 genes The operator is the on/off switch The operon is a set of genes that code for enzymes involved in the same function RNA polymerase attached to DNA at the promoter and begins to transcribe It will continue until it reaches the repressor, a protein that binds the operator and blocks RNA polymerase Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Eukaryotes have 30,000 genes and the process is more complicated They have a promoter, enhancer, and activator The enhancer is a sequence of DNA that can be bound by transcription factors (TF, a protein that controls transcription) Eukaryotic Gene Regulation The activator attaches to the enhancer and causes a loop to form bringing the enhancer close to the promoter by being in contact with the TF RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter and beings transcription