* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries
Survey
Document related concepts
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
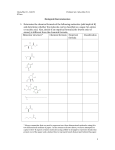
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries (email: [email protected] ) 3 September 2014 MAIN CONCEPTS TO PULL FROM CHAPTER 2: * SHAPE DETERMINES FUNCTION 1.Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called ________________. 2.Which kind of bond holds atoms in a water molecule together? What attracts water molecules to one another? 3.Isotopes of an element differ from each other in the number of: (circle one) a. protons in the nucleus b. neutrons in the nucleus c. electrons in the outer shells d. a, b, and c are all correct 4.The number and arrangement of electrons in an atom’s outer energy level determines the atom’s a. atomic weight b. atomic number c. molecular weight d. chemical properties 5.All the chemical reactions that occur in the human body are collectively referred to as: a. anabolism b. catabolism c. metabolism d. homeostasis 6.What are the four major elements of the human body: (list from most abundant to least abundant) 1. 2. 3. 4. 7.Acids release _______ and are therefore proton ___________ (Example: HCl H+ + Cl-) 8.Bases release _________ and are therefore proton ________________ (Example: NaOH Na+ + OH-) SIDE NOTE: Most Physiological systems contain weak acids and weak bases 9.What is the normal range for the pH of human blood? 10.List the 4 organic compounds highlighted in chapter 2. 1. 2. 3. 4. 11.Carbohydrates contain what 3 major elements? 1. 2. 3. Questions 12-14: Complex Sugars: 12.Glucose + Fructose = __________________ 13. ______________ + Glucose = Maltose 14.Galactose + _____________ = Lactose 15.Neutral fats or Triglycerides are composed of _________ Fatty Acids bonded to a glycerol molecule 16.A dehydration synthesis reaction between glycerol and a single fatty acid would yield a(n) a. micelle b. monoglyceride c. triglyceride d. omega – 3 fatty acid e. diglyceride 17.How does boiling a protein affect its structural and functional properties? 18.On average, lipids provide roughly twice as much energy as carbohydrates do, gram for gram, when broken down in the body. T/F 19. Of the 20 common Amino Acids the body can synthesize __________ of them (nonessential) and the remaining ________ amino acids need to be obtained from our diet (essential) 20.Each Amino Acid consists of 5 components. List all 5 components 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 21.List (from simplest to most complex) the four levels of structural complexity that proteins can have: 1. 2. 3. 4. 22.__________________ proteins form extended sheets or strands. These proteins are tough, durable and generally insoluble in water; in the body, they usually play structural roles (example: keratin, collagen) 23.__________________ proteins are compact, generally rounded, and readily enter an aqueous solution. These proteins are enzymes, hormones, and other molecules that circulate in the bloodstream, as well as, the enzymes that control chemical reactions inside cells. (example: Myoglobin, Hemoglobin) Important terms defined: Dehydration synthesis: The joining of two molecules associated with the removal of a water molecule Hydrolysis: The breakage of a chemical bond through the addition of a water molecule; the reverse of dehydration synthesis Hydrophilic: freely associating with water; readily entering into solution; water loving Hydrophobic: Incapable of freely associating with water molecules; insoluble; water-fearing REMINDERS: 1. Exam 1 (ch. 1-3) on Monday, September 8th!!!!! (P.S. that’s in 5 days!!!) 2. Chapter 3 worksheet/ Review session tomorrow – come prepared with questions you would like clarified before the exam 3. Shoot me an email with any further questions you may have this weekend (email: [email protected]) “The difference between a successful person and others is not a lack of strength, not a lack of knowledge, but rather in a lack of will” – Vincent T. Lombardi