* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15 Evolution KL updated
Survey
Document related concepts
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
On the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
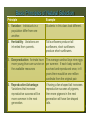
Chapter 15 Evolution 15.1 Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection 15.2 Evidence of Evolution 15.3 Shaping Evolutionary Theory 15.1 Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection ! Main idea: Charles Darwin developed a theory of evolution based on natural selection ! Objectives n Discuss the evidence that convinced Darwin that species could change over time. n List the four principles of natural selection. n Show how natural selection could change a population ! New Vocabulary n Selective breeding, Artificial selection, Natural selection, Evolution Developing the Theory of Natural Selection ! Charles Darwin boarded the HMS Beagle in 1831. ! Most believed the world was about 6,000 years old. ! During the ship’s five year voyage, Darwin made extensive collections of rocks, fossils, plants and animals. ! He also read Charles Lyell’s Principles of Geology – a book proposing the Earth was millions of years old. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection HMS Beagle ! In 1835, the Beagle arrived in the Galapagos Islands off the coast of South America. ! Darwin began to collect mockingbirds, finches, and other animals on the four islands. ! He noticed that the different islands seemed to have their own, slightly different varieties of animals. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection Galápagos Islands ! Almost every specimen that Darwin had collected on the islands was new to European scientists. ! Darwin suspected populations from the mainland changed after reaching the Galápagos. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection ! Darwin hypothesized that new species could appear gradually through small changes in ancestral species. ! Darwin inferred that if humans could change species by artificial selection (selective breeding), then perhaps the same process could work in nature. Developing the Theory of Natural Selection Natural Selection ! Darwin called his theory Natural Selection ! He reasoned that, given enough time, natural selection could modify a population enough to produce a new species. Basic Principles of Natural Selection Principle Example 1. Variation: Individuals in a population differ from one another. Students in this class look different. 2. Heritability: Variations are inherited from parents. Tall sunflowers produce tall sunflowers, short sunflowers produce short sunflowers. 3. Overproduction: Animals have The average cardinal lays nine eggs more young than can survive on per summer. If each baby cardinal the available resources survived and reproduced once, in 8 years there would be one million cardinals from the original pair. 4. Reproductive Advantage: Variations that increase reproductive success will be more common in the next generation. If having a fan-shaped tail increases reproductive success of pigeons, then more pigeons in the next generation will have fan-shaped tails. The Origin of Species ! Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859. ! Today, biologists use the term evolution to define changes in groups of organisms through time. ! Darwin’s theory of natural selection is NOT the same as evolution. Natural selection is a means of explaining HOW evolution works. 15.2 Evidence of Evolution ! Main idea: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. ! Objectives: n Describe how fossils provide evidence of evolution. n Discuss morphological evidence of evolution. n Explain how physiology and biochemistry provide evidence of evolution. ! New Vocabulary n Derived trait n Ancestral trait n Homologous structure n Vestigial structure n Analogous structure n n n n Embryo Fitness Mimicry Camouflage