* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
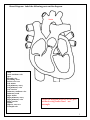
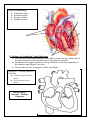
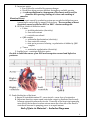
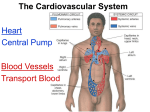
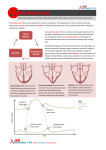
A&P Notes: The Heart I. Heart Anatomy: Your Objectives: Determine the size & location of the heart. Determine the function/importance/description of each of the following parts. Determine the location of the parts on a heart diagram Heart location and size Weight in lbs and grams _______________________________________ Location in chest (give landmarks to describe) Heart Structures: Heart Wall & Pericardial Cavity o Pericardial cavity o Parietal pericardium o Visceral pericardium (aka. Epicardium) o Myocardium o Endocardium Chambers & associated structures o Atrium (atria = plural) o Auricle o Pectinate muscles o Ventricles o Trabeculae carnae o Chordate tendinae & Papillary muscles o Septum Valves and associated structures o Atrioventricular valves Tricuspid Bicuspid (aka. Mitral) o Semilunar valves Pulmonary SL Aortic SL o Know how valves open & close to prevent backflow of blood which is important in keeping oxygenated & deoxygenated blood from mixing and gets them to the right structures. o What is the first heart sound caused by? o What is the second heart sound caused by? 1 Blood vessels (major) o Superior vena cava o Inferior vena cava o Pulmonary trunk o Pulmonary arteries (right and left) o Pulmonary veins (right and left) o Aorta (ascending, descending, arch) Fetal structures – what is the purpose of these 2 structures in a fetal heart? o Foramen ovale o Ductus arteriosus 1. Why are the circulatory system organs lined with endothelium? 2. Which chamber has thickest most muscular walls and why? 3. What is the purpose of the 4 valves? 4. What do these fetal structures become in the adult heart? When does this occur? a. Foramen ovale b. Ductus arteriosum 2 Heart Diagram: Label the following parts on this diagram. Aorta Aorta Aortic semilunar valve Apex Bicuspid valve Descending Aorta Inferior vena cava Left Atrium Left pulmonary artery Left pulmonary veins Left Ventricle Pulmonary semilunar valve Pulmonary trunk Right Atrium Right pulmonary artery Right pulmonary veins Right Ventricle Septum Superior vena cava Tricuspid valve Label the diagram directly on the part without using leader lines: see example 3 Label the following: Trabeculae carnae Pectinate muscles Chordae tendinae Papillary muscles II. Pathway of circulation: Your Objectives Differentiate between pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit: which side of the heart is involved in each and what is the purpose of each? Determine the complete pathway a drop of blood would take beginning in the superior and inferior vena cava Discuss the need for a separate cardiac circulation. Diagram #2 – Trace the pathway of blood flow Use blue arrows for deoxy blood Use red arrows for oxy blood End of Quiz #1 Material – Includes Diagrams 4 Two events happen in a heart beat 1. electrical event which causes: 2. muscular event/contraction Either event can have problems so doctors need the ability to check each one. The Conduction system I. Conduction System of the Heart - Know parts on diagram Cardiac muscle needs organization/rhythm and speed control for maximum efficiency- So two controlling/coordinating systems are needed: A. autonomic nervous system divisions 1. sympathetic NS - increase rate & force 2. parasympathetic NS - decrease heart rate & force B. Intrinsic conduction system 1. gap junctions 2. conduction system parts a. sinoatrial (SA) node b. atrioventricular (AV) node c. AV bundle & bundle branches d. Purkinje fibers Muscular event – the Cardiac Cycle I. alternate contraction and relaxation of heart 1. described in terms of ventricular events 2. systole - contraction 3. diastole - relaxation II. Phases of cardiac cycle A. mid to late diastole (heart is in complete relaxation) - ventricular filling 1. pressure in heart is low - blood flows passively into atria then ventricles 2. AV valves open - semilunar valves closed 3. 70% of ventricular filling occurs 4. atria begin to contract forcing remaining 30% of blood into ventricles 5. pressure in ventricles begins to close AV valves B. ventricular systole 1. BP in ventricles rises sharply - closes AV valves atrial begin filling again 2. isovolumetric contraction phase a. while both sets of valves are closed - the muscle contracts which builds pressure for a very short time period 3. BP exceeds BP in aorta & pulmonary trunk and forces SL valves open 4. ventricular ejection phase a. blood expelled into aorta and pulmonary trunk b. normal aorta pressure is 120 mm Hg C. Early diastole / isovolumetric relaxation phase 1. ventricles relax and pressure drops 2. blood backflow closes semilunar valves 1. atrial pressure will then force open AV valves D. Cardiac cycle = 0.8 secs 1. atria systole = 0.1 secs 2. vent systole = 0.3 secs 3. total heart relaxation (quiescent period) = 0.4 secs only time heart gets to relax 5 E. Important points 1. flow of blood is controlled by pressure changes 2. blood flows along pressure gradient through any available opening 3. An echocardiogram is a sonogram of the heart and is used to visualize the opening/closing of valves and working of muscles Electrical Event A. electrical events caused by conducting system are recorded as deflection waves transmitted to entire body by means of electrolytes. The recording of heart electrical waves is called an ECG or EKG - electrocardiogram B. ECG has 3 kinds of deflection waves 1. P wave a. atrial depolarization (electricity) b. then atria contract c. ventricles are relaxed 2. QRS complex a. ventricular depolarization (electricity) b. then ventricles contract c. atria are in process of relaxing - repolarization is hidden by QRS complex 3. T wave a. ventricular repolarization (electricity) C. healthy heart - consistant deflection waves Be able to label the waves of an ECG and recognize normal and defective patterns. II. Frank-Starling law of the heart A. degree of stretch determines SV - more stretch = more force of contraction B. Important function: ensure equal ventricular output to distribute blood evenly between systemic & pulmonary circuits. If one side of the heart starts pumping more blood, the increase in venous return causes the other side of the heart to stretch and increase its pumping power to an equal amount End of Quiz #2 Material – Includes Diagrams 6 Heart Disorders angina pectoris arteriosclerosis (atherosclerosis) bradycardia cardiac tamponade congenital heart defects 1. patent ductus arteriosus 2. septal defect 3. tetralogy of Fallot congestive heart failure 1. pulmonary congestion 2. peripheral congestion cor pulmonale decompensated heart ectopic focus extrasystole fibrillation heart block heart murmur heart palpitation incompetent valve mitral valve prolapse myocardial infarction myocarditis pericarditis tachycardia valvular stenosis 7